(Ubuntu: Lesson 13)
{ Installing and Testing denyhosts and brutessh.py }
| Section 0. Background Information |
- What is denyhosts
- DenyHosts is a log-based intrusion prevention security tool for SSH servers written in Python. It is intended to prevent brute force attacks on SSH servers by monitoring invalid login attempts in the authentication log and blocking the originating IP addresses.
- http://denyhosts.sourceforge.net/
- What is brutessh.py
- Brutessh is a program that uses the paramiko ssh library, to launch bruteforce passwords attacks to the sshd service. The tools is multithreading and uses a dictionary for the passwords.
- Prerequisite
- Ubuntu: Lesson 1: Installing Ubuntu Desktop 12.04 LTS
- Ubuntu: Lesson 8: Installing and Securing openssh-server (a.k.a., sshd)
- BackTrack: Lesson 1: Installing BackTrack 5 R1
-
Lab Notes
- In this lab we will how to do the following:
- We will install denyhosts on Ubuntu.
- We will install brutessh.py on BackTrack.
- We will use brutessh on BackTrack to attack Ubuntu.
- In this lab we will how to do the following:
- Legal Disclaimer
- As a condition of your use of this Web site, you warrant to computersecuritystudent.com that you will not use this Web site for any purpose that is unlawful or that is prohibited by these terms, conditions, and notices.
- In accordance with UCC § 2-316, this product is provided with "no warranties, either express or implied." The information contained is provided "as-is", with "no guarantee of merchantability."
- In addition, this is a teaching website that does not condone malicious behavior of any kind.
- You are on notice, that continuing and/or using this lab outside your "own" test environment is considered malicious and is against the law.
- © 2012 No content replication of any kind is allowed without express written permission.
| Section 1: Start Ubuntu 12.04 |
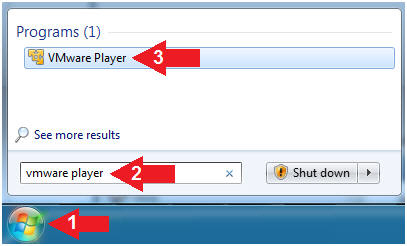
- Start VMware Player
- Instructions
- For Windows 7
- Click Start Button
- Search for "vmware player"
- Click VMware Player
- For Windows XP
- Starts --> Programs --> VMware Player
- For Windows 7
- Instructions
- Verify Virtual Machine Settings.
- Instructions
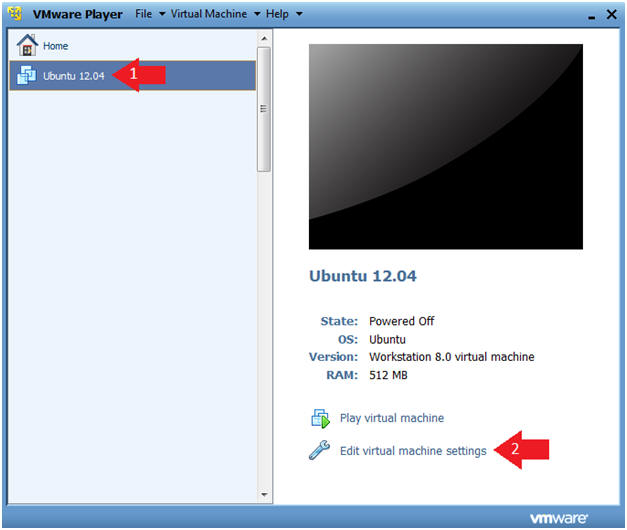
- Click on Ubuntu 12.04
- Click on Edit virtual machine settings
- Instructions
- Configure Network Adapter
- Instructions
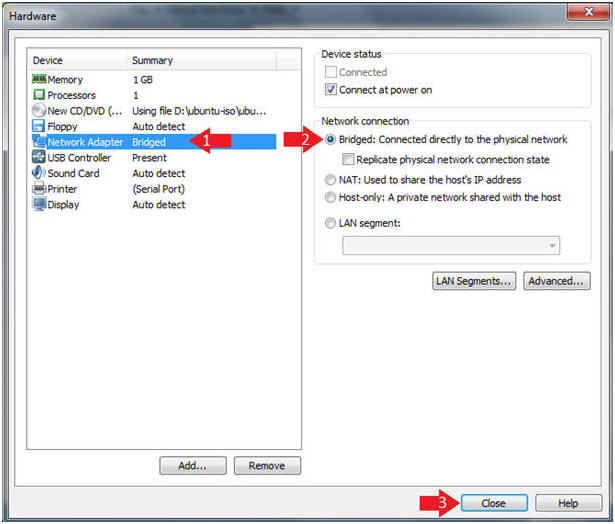
- Click on Network Adapter
- Click on the Bridged Radio Button
- Click on the Close Button
- Instructions
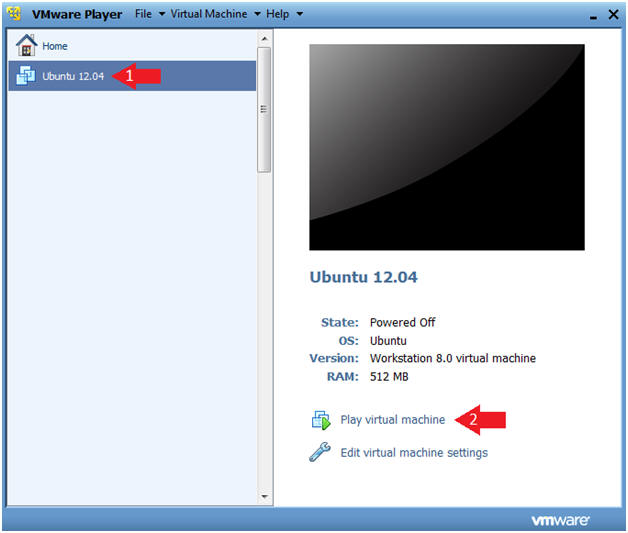
- Start the Ubuntu 12.04 VM
- Instructions
- Click on Ubuntu 12.04
- Click on Play virtual machine
- Instructions
| Section 2: Login to Ubuntu |
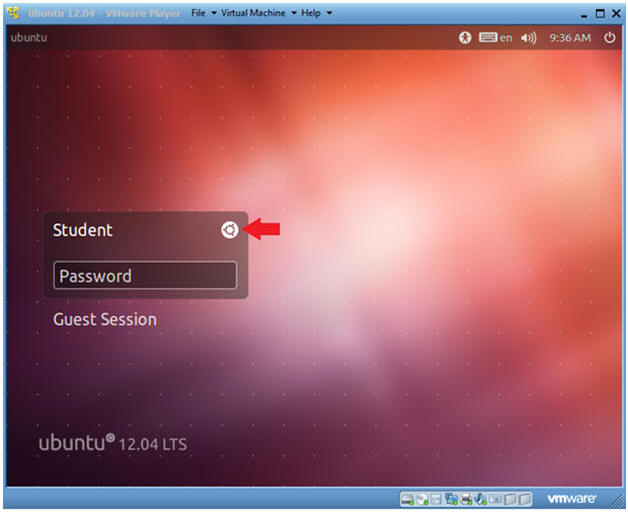
- Change to Gnome Classic
- Instructions:
- Click on the Circle
- Instructions:
- Select Gnome Classic
- Instructions:
- Double Click on GNOME Classic
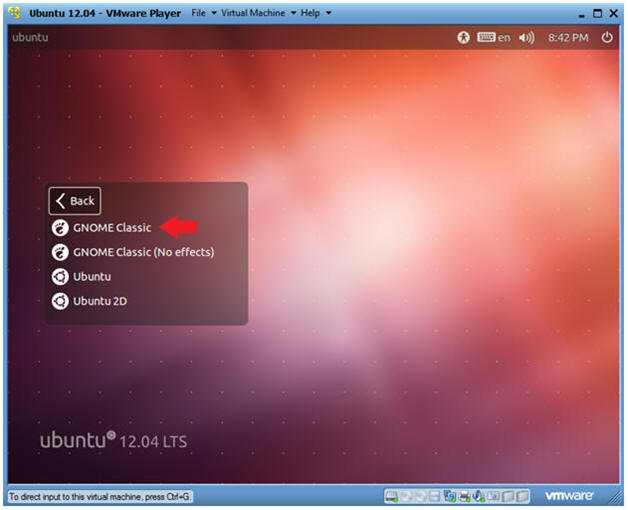
- Instructions:
- Login to Server
- Instructions
- User: Student
- Password: Please supply the student password.
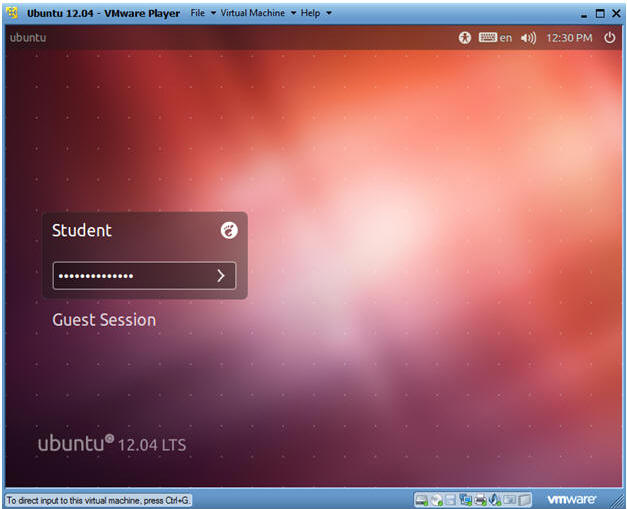
- Instructions
| Section 3: Become Root and Verify Network Connection |
- Start up a Terminal
- Instructions
- Click on the Terminal
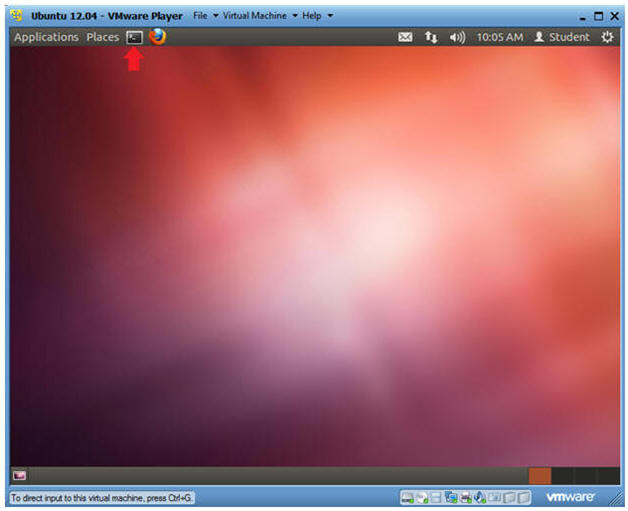
- Instructions
- Become Root
- Instructions
- sudo su -
- Supply the student password.
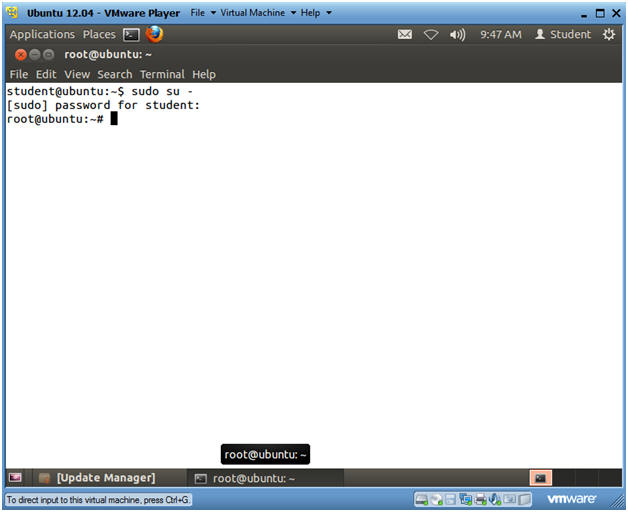
- Instructions
- Verify you have a network connection
- Instructions
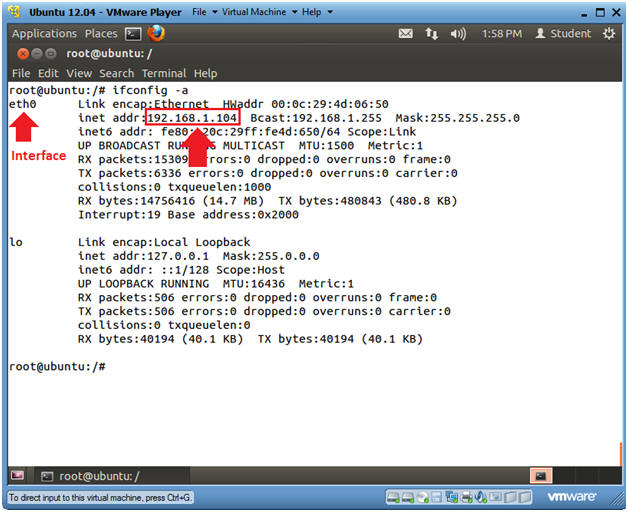
- ifconfig -a
- eth0 is the name of my interface.
- 192.168.1.104 is my network IP address.
- ifconfig -a
- Note(FYI):
- If you do not have an DHCP IP Address
try the following:
- dhclient
- OR
- /etc/init.d/networking restart
- dhclient
- If you do not have an DHCP IP Address
try the following:
- Instructions
| Section 3: Update apt-get's package index |
- Update apt-get's package index
- Instructions
- apt-get update
- Note(FYI):
- update is used to resynchronize the package index files from their sources. I.e., The "update" flag updates apt-get's local database with debian server's pkglist files. The indexes of available packages are fetched from the location(s) specified in /etc/apt/sources.list.
- Instructions
| Section 4: Search for denyhosts |
- Search for denyhosts
- Instructions
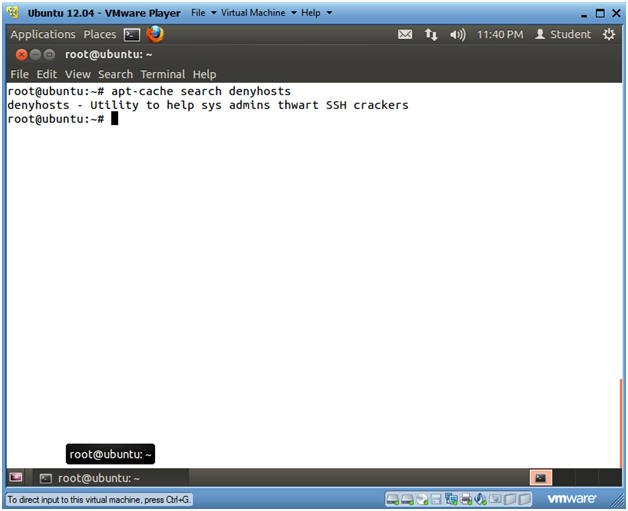
- apt-cache search denyhosts
- Note(FYI):
- apt-cache is a command to manipulate and obtain information from the ubuntu packages.
- Instructions
| Section 5: Install denyhosts |
- Install denyhosts
- Instructions
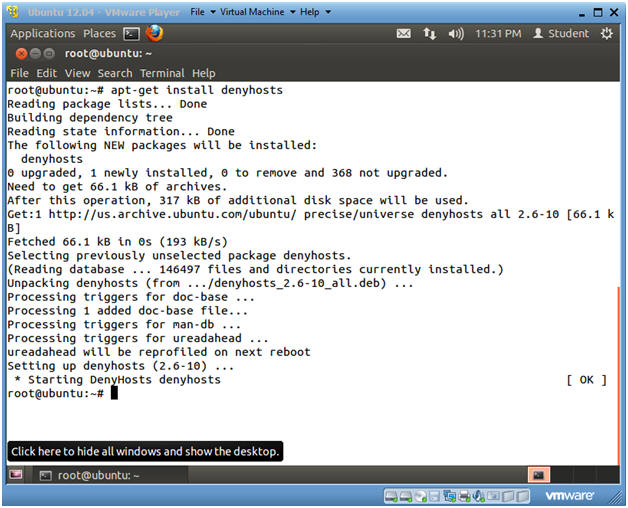
- apt-get install denyhosts
- Instructions
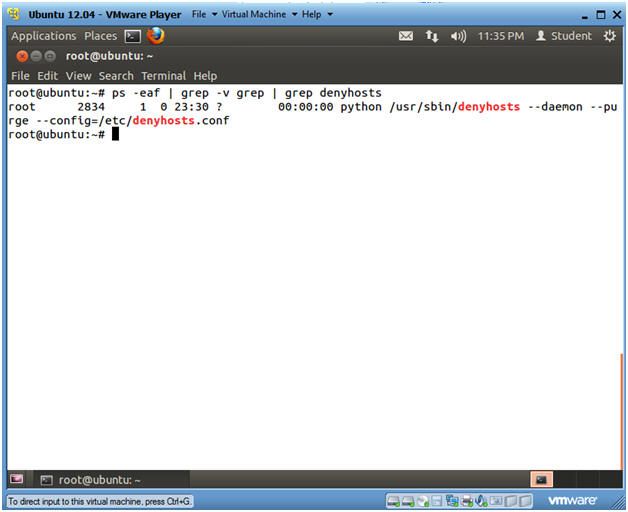
- Verify that denyhosts is installed and is
running
- Instructions
- ps -eaf | grep -v grep | grep denyhosts
- ps -eaf, show all processes.
- grep -v grep, filter out the grep process.
- grep denyhosts, show only the denyhosts process.
- ps -eaf | grep -v grep | grep denyhosts
- Instructions
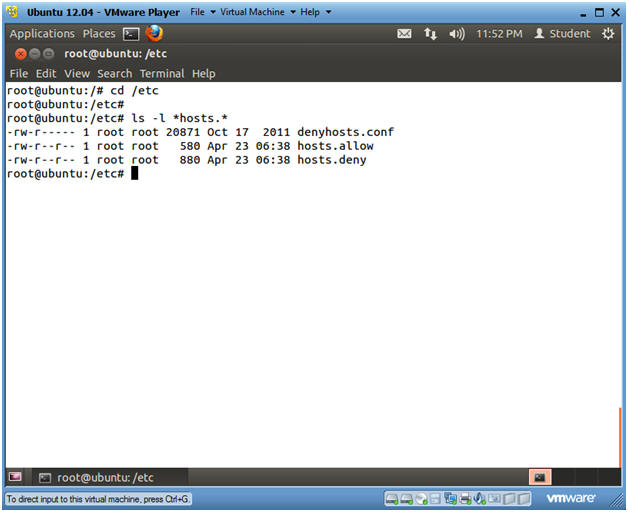
- View host files
- Instructions
- cd /etc
- ls -l *hosts.*
- Note(FYI):
- denyhosts.conf,
- This is the denyhosts configuration file.
- hosts.allow
- If you add a host to this file, beware that all other hosts not in this file will be denied access.
- hosts.deny
- If a host is included in this file, then it will be denied access.
- denyhosts.conf,
- Instructions
| Section 6: Startup Script for denyhosts |
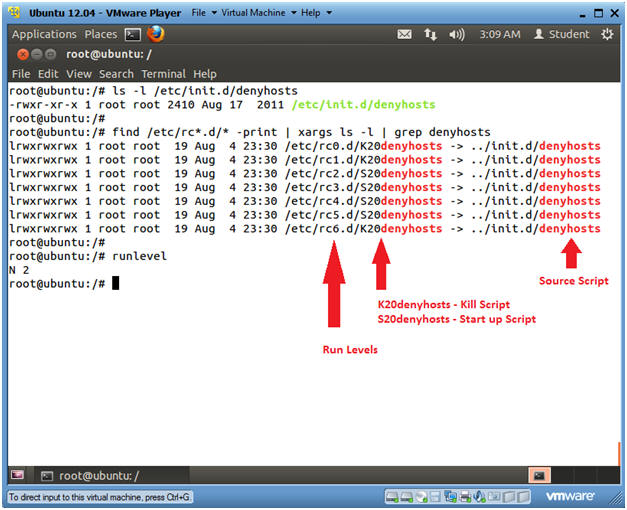
- Startup Script for denyhosts
- Instructions
- ls -l /etc/init.d/denyhosts
- As part of the denyhosts installation, the denyhosts startup script is placed in /etc/init.d/denyhosts.
- find /etc/rc*.d/* -print | xargs ls -l
| grep denyhosts
- Identifies start up and kill scripts for denyhosts.
- runlevel
- Identifies the current run level.
- 0 System Halt
- 1 Single user
- 2 Full multi-user mode (Default)
- 3-5 Same as 2
- 6 System Reboot
- Identifies the current run level.
- ls -l /etc/init.d/denyhosts
- Instructions
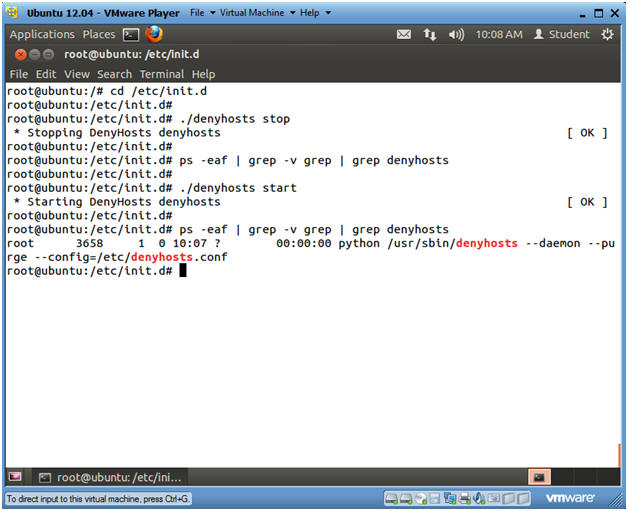
- Stopping and Starting denyhosts with /etc/init.d/denyhosts
- Instructions
- cd /etc/init.d
- ./denyhosts stop
- ps -eaf | grep -v grep | grep denyhosts
- Notice, that no lines are returned, because denyhostsis not running.
- ./denyhosts start
- ps -eaf | grep -v grep | grep denyhosts
- Now one line is returned, because denyhosts is running.
- Instructions
- Stopping and Starting DENYHOSTS with the "service"
command
- Instructions
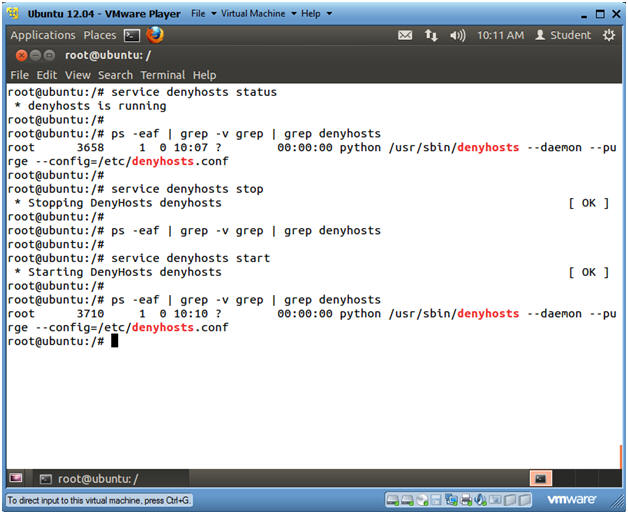
- service denyhosts status
- This will show if denyhosts is running or not.
- ps -eaf | grep -v grep | grep denyhosts
- This will show the denyhosts process.
- service denyhosts stop
- This command will stop the denyhosts daemon.
- ps -eaf | grep -v grep | grep denyhosts
- This will show there is NO denyhosts process running.
- service denyhosts start
- This will start the denyhosts daemon/service.
- ps -eaf | grep -v grep | grep denyhosts
- This will show the denyhosts process.
- service denyhosts status
- Instructions
| Section 7: Configure BackTrack Virtual Machine Settings |
- Start VMware Player
- Instructions
- For Windows 7
- Click Start Button
- Search for "vmware player"
- Click VMware Player
- For Windows XP
- Starts --> Programs --> VMware Player
- For Windows 7

- Instructions
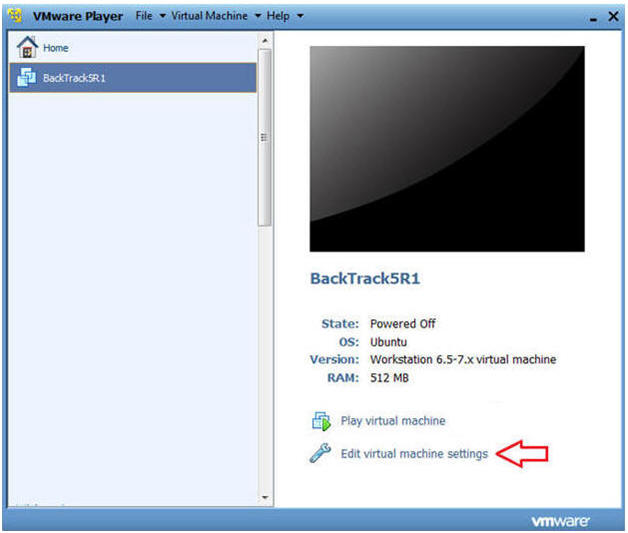
- Edit BackTrack Virtual Machine Settings
- Instructions:
- Highlight BackTrack5R1
- Click Edit virtual machine settings
- Instructions:
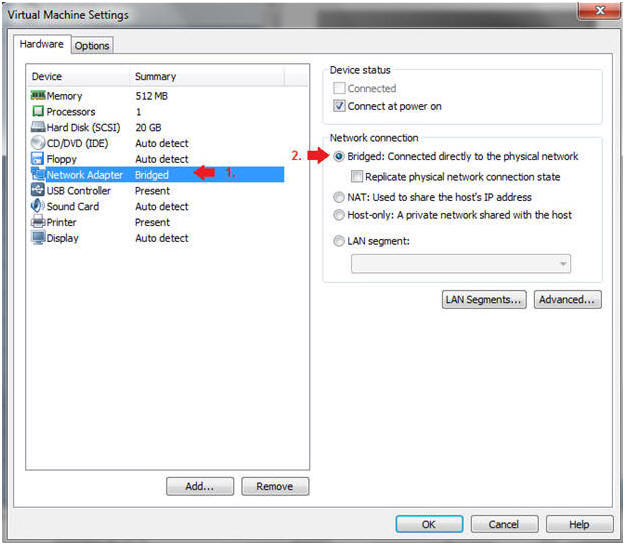
- Edit Network Adapter
- Instructions:
- Highlight Network Adapter
- Select Bridged
- Do not Click on the OK Button.
- Instructions:
| Section 8: Login to BackTrack |
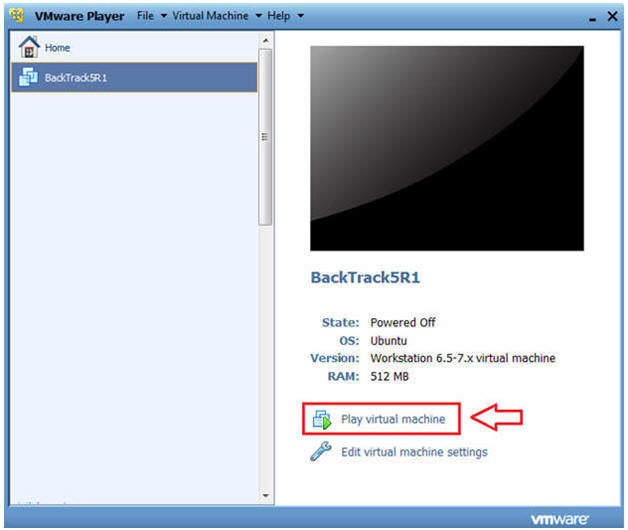
- Start BackTrack VM Instance
- Instructions:
- Start Up VMWare Player
- Select BackTrack5R1
- Play virtual machine
- Instructions:
- Login to BackTrack
- Instructions:
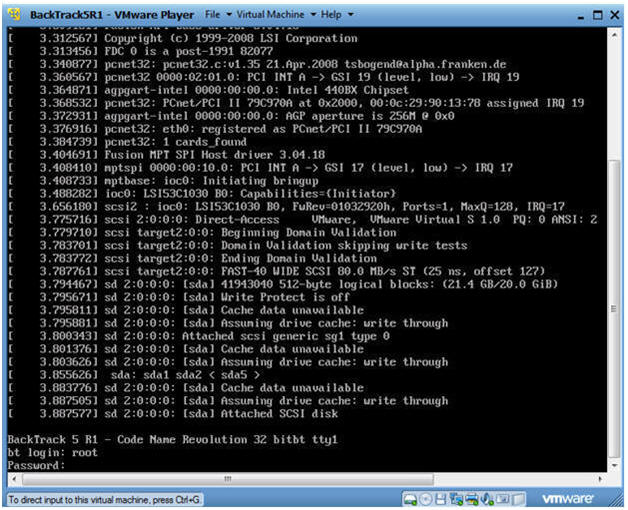
- Login: root
- Password: toor or <whatever you changed it to>.
- Instructions:
- Bring up the GNOME
- Instructions:
- Type startx
- Instructions:
| Section 9: Open Console Terminal and Retrieve IP Address |
- Open a console terminal
- Instructions:
- Click on the console terminal
- Instructions:
- Get IP Address
- Instructions:
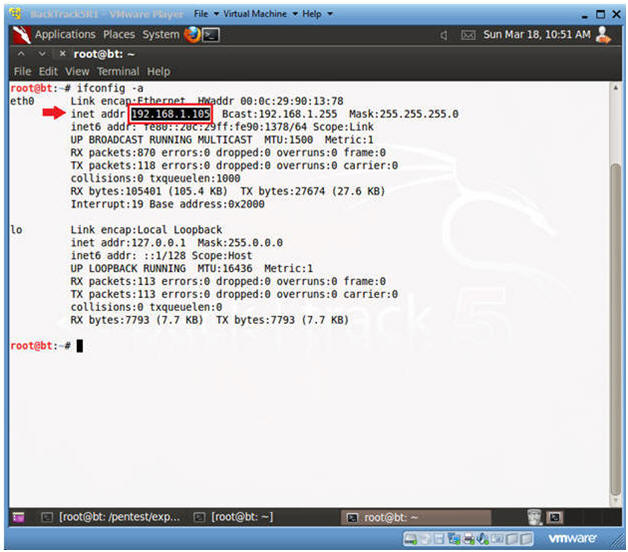
- ifconfig -a
- Note(FYI):
- As indicated below, my IP address is 192.168.1.105.
- Please record your IP address.
- Instructions:
| Section 10: Test SSH Between BackTrack and Ubuntu |
- Test SSH from Backtrack to Ubuntu
- Note(FYI):
- Issue the below commands from the BackTrack Terminal.
- Instructions:
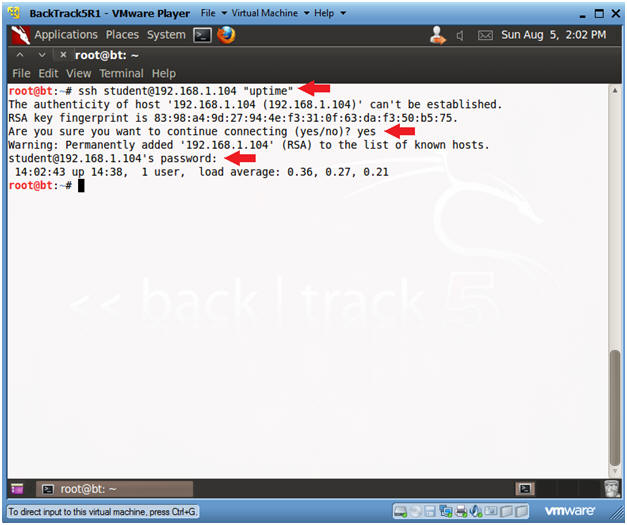
- ssh
student@192.168.1.104
"uptime"
- If you do not have a student account on ubuntu, replace it with the system account you create in Lab 1.
- Replace 192.168.1.104 with Ubuntu's IP address you obtained in (Section 3, Step 3).
- connecting (yes/no)? yes
- Provide Password
- ssh
student@192.168.1.104
"uptime"
- Note(FYI):
- Check Ubuntu's auth.log
- Note(FYI):
- Issue the below commands from the Ubuntu Terminal.
- Instructions:
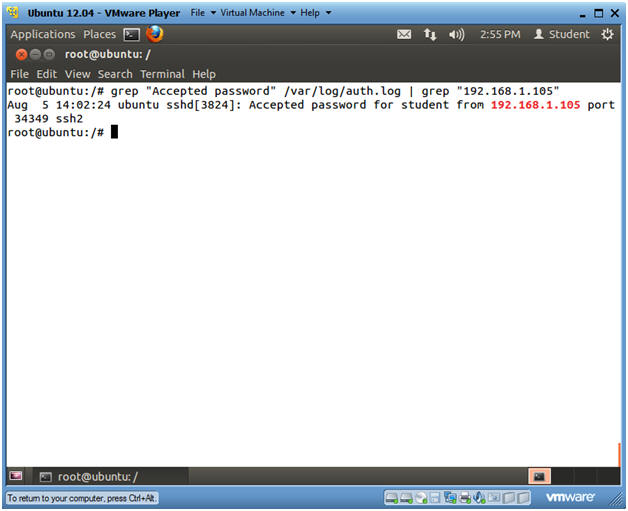
- grep "Accepted password" /var/log/auth.log
| grep "192.168.1.105"
- Replace 192.168.1.105 with BackTrack's IP Address obtained in (Section 9, Step 2).
- grep "Accepted password" /var/log/auth.log
| grep "192.168.1.105"
- Note(FYI):
| Section 11: Install and run BruteSSH.py against Ubuntu |
- Search for BruteSSH.py
- Note(FYI):
- Issue the below commands from the BackTrack Terminal.
- Instructions:
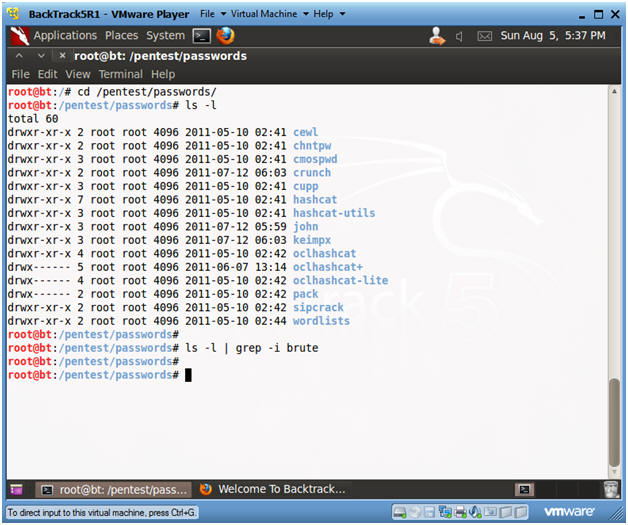
- cd /pentest/passwords/
- In BackTrack, the password cracking programs are typically located in this directory.
- ls -l
- ls -l | grep -i brute
- Our search for brute does not return results.
- cd /pentest/passwords/
- Note(FYI):
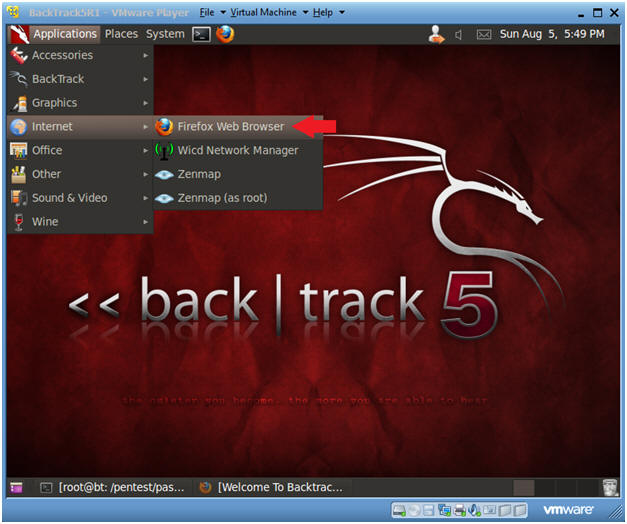
- Start Firefox
- Instructions:
- Applications --> Internet --> Firefox Web Browser
- Instructions:
- Download brutessh
- Instructions:
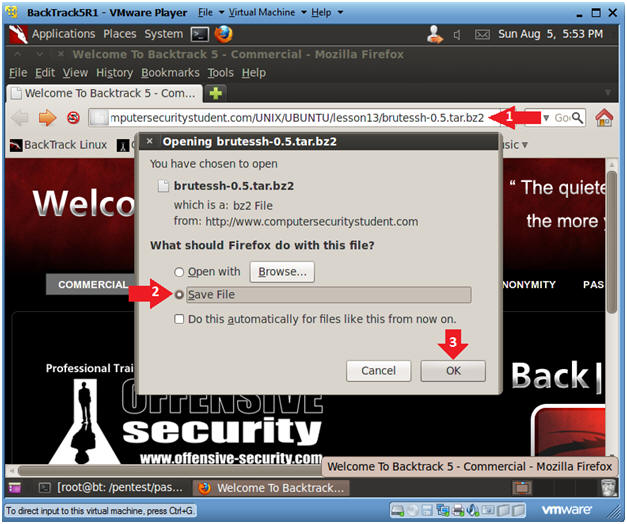
- Place the below URL in the address box
and Press Enter
- http://www.computersecuritystudent.com/UNIX/UBUNTU/1204/lesson13/brutessh-0.5.tar.bz2
- Click the Save File radio button
- Click OK
- Place the below URL in the address box
and Press Enter
- Instructions:
- Save to /pentest/passwords
- Instructions:
- Click on Browse for other folders
- Click on File System
- Navigate to /pentest/passwords
- Click Save
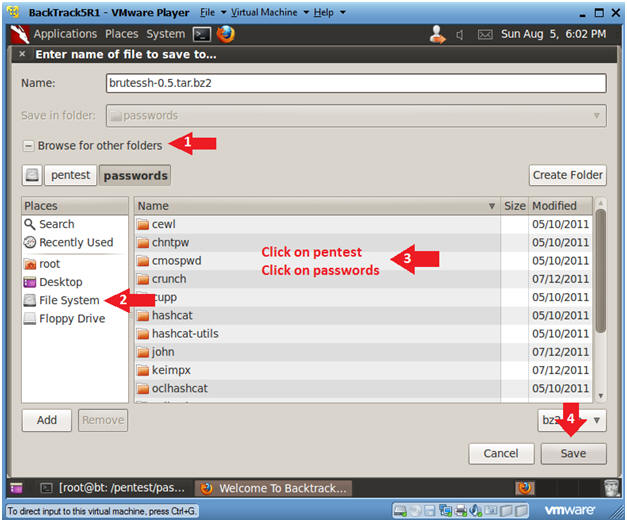
- Instructions:
- Unzip brutessh-0.5.tar.bz2
- Instructions:
- cd /pentest/passwords/
- ls -l brutessh-0.5.tar.bz2
- bunzip2 brutessh-0.5.tar.bz2
- ls -l brutessh-0.5.tar
- tar xovf brutessh-0.5.tar
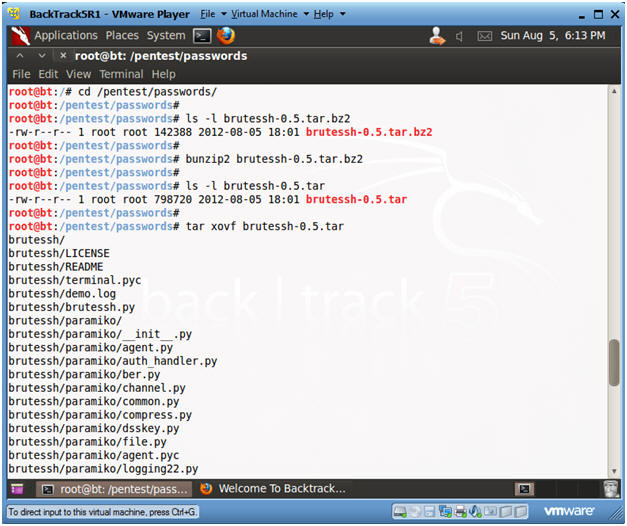
- Instructions:
- BruteSSH House Cleaning
- Instructions:
- cd /pentest/passwords/
- rm brutessh-0.5.tar
- We no longer need the tar file.
- cd brutessh/
- ls -la
- cat /pentest/passwords/john/password.lst
| grep -v "^#" | head -50 > password.txt
- I grabbed the first 50 passwords from John the Ripper to create enough future brute force ssh traffic for denyhosts to block.
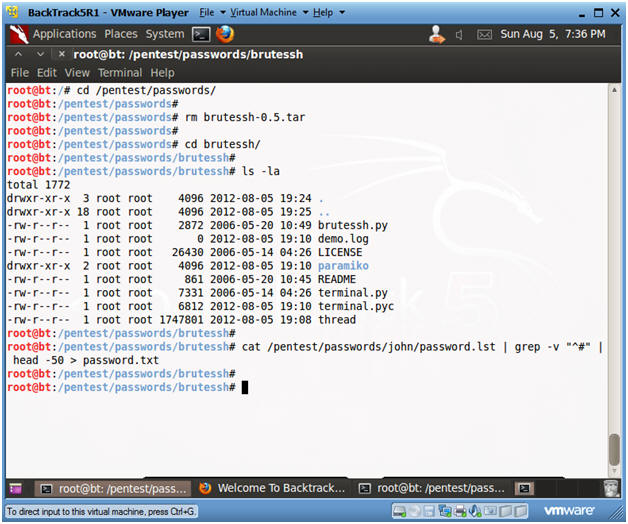
- Instructions:
- Using BruteSSH
- Instructions:
- python brutessh.py -help
- The -help flag produced the usage options.
- python brutessh.py -help
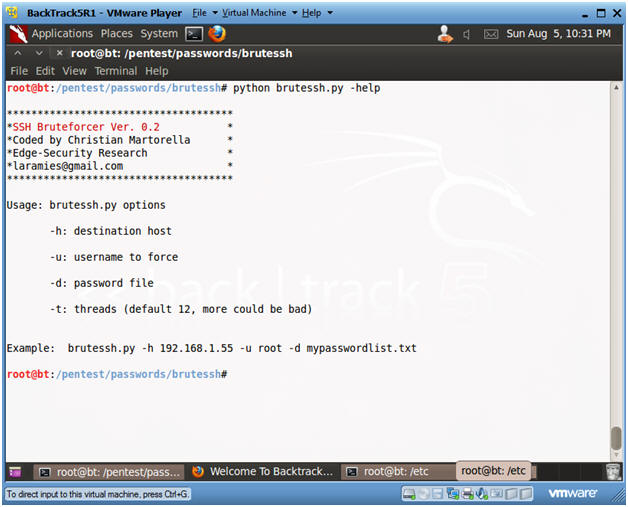
- Instructions:
- Using BruteSSH Against DenyHosts
- Instructions:
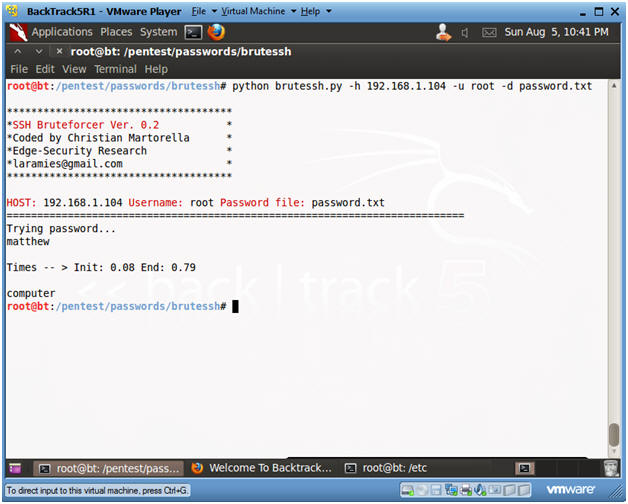
- python brutessh.py -h
192.168.1.104 -u root -d password.txt
- 192.168.1.104 is the IP address of the victim Ubuntu machine in my case. Refer to (Section 3, Step 3) to obtain Ubuntu IP Address.
- python brutessh.py -h
192.168.1.104 -u root -d password.txt
- Instructions:
| Section 12: Testing Blocked SSH Traffic from BackTrack to Ubuntu |
- Testing Blocked SSH Connection
- Instructions:
- ssh
student@192.168.1.104
- If you do not have a student account on ubuntu, replace it with the system account you created in Lab 1.
- Replace 192.168.1.104 with Ubuntu's IP address you obtained in (Section 3, Step 3).
- Note: DenyHosts on the Ubuntu server is now blocking the ssh protocol from connecting to port 22.
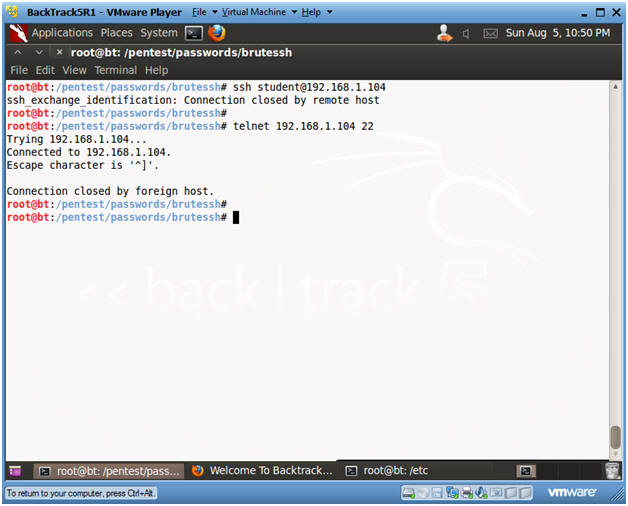
- telnet 192.168.1.104 22
- Here I am testing to see if IP Addressed is really blocked or if just SSH traffic is blocked.
- Note: Although BackTrack SSH traffic is now blocked, it is still possible to connect use TCP over port 22.
- ssh
student@192.168.1.104
- Instructions:
| Section 13: Proof of Lab && Analyzing Ubuntu Deny Host Logs |
- Analyzing Ubuntu Deny Host Logs
- Note(FYI):
- Make sure you are on the Ubuntu Server.
- You will be analyzing Ubuntu log files.
- Instructions:
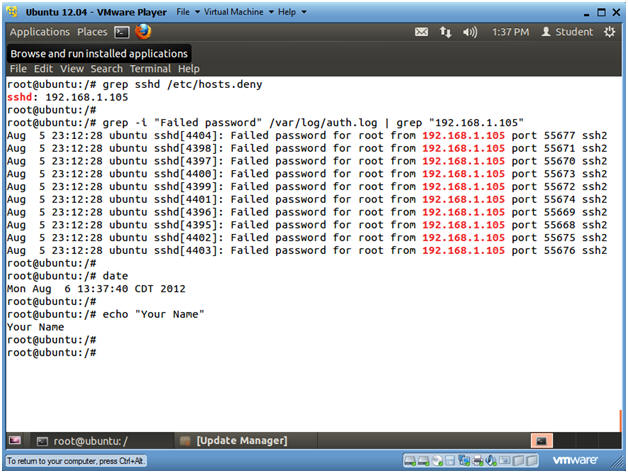
- grep sshd /etc/hosts.deny
- The hosts.deny file contains all the ports that have been blocked by the denyhosts daemon.
- grep -i "Failed password" /var/log/auth.log
| grep "192.168.1.105"
- Replace 192.168.1.105 with BackTrack's IP Address obtained in (Section 9, Step 2).
- date
- echo "Your Name"
- Replace the string "Your Name" with your actual name.
- e.g., echo "John Gray"
- grep sshd /etc/hosts.deny
-
Proof of Lab Instructions
- Press both the <Ctrl> and <Alt> keys at the same time.
- Do a <PrtScn>
- Paste into a word document
- Upload to Moodle
- Note(FYI):
| Section 14: Unblock BackTrack |
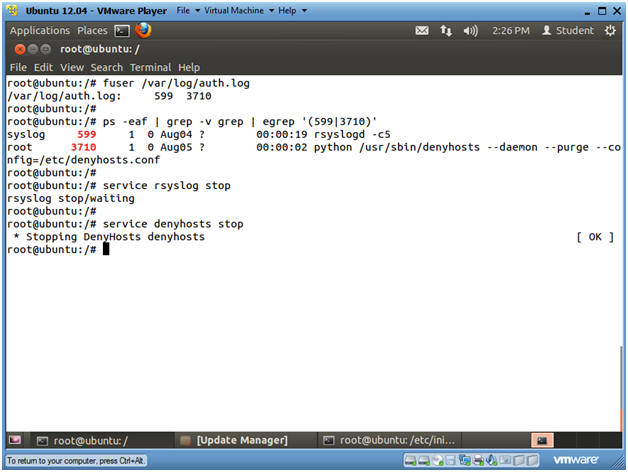
- Stop rsyslog and denyhosts
- Note(FYI):
- Make sure you are on the Ubuntu Server.
- Instructions:
- fuser /var/log/auth.log
- service rsyslog stop
- service denyhosts stop
- Note(FYI):
- Scrub the hosts.deny file
- Instructions:
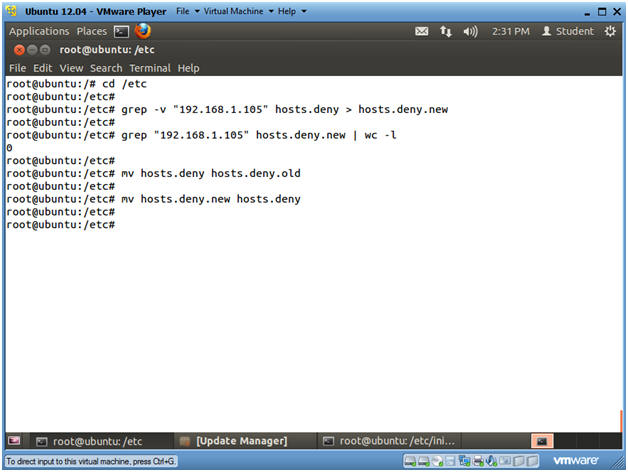
- cd /etc
- grep -v "192.168.1.105"
hosts.deny > hosts.deny.new
- Replace 192.168.1.105 with BackTrack's IP Address obtained in (Section 9, Step 2).
- grep "192.168.1.105"
hosts.deny.new | wc -l
- Replace 192.168.1.105 with BackTrack's IP Address obtained in (Section 9, Step 2).
- mv hosts.deny hosts.deny.old
- mv hosts.deny.new hosts.deny
- Instructions:
- Scrub the auth.log file
- Instructions:
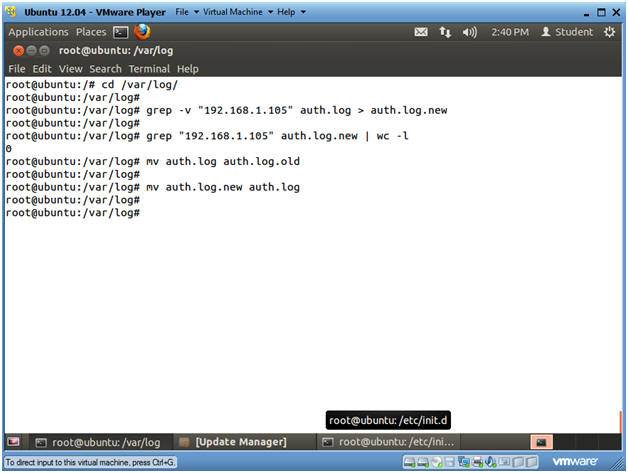
- cd /var/log/
- grep -v "192.168.1.105"
auth.log > auth.log.new
- Replace 192.168.1.105 with BackTrack's IP Address obtained in (Section 9, Step 2).
- grep "192.168.1.105"
auth.log.new | wc -l
- Replace 192.168.1.105 with BackTrack's IP Address obtained in (Section 9, Step 2).
- mv auth.log auth.log.old
- mv auth.log.new auth.log
- Instructions:
- Scrub the denyhosts file
- Instructions:
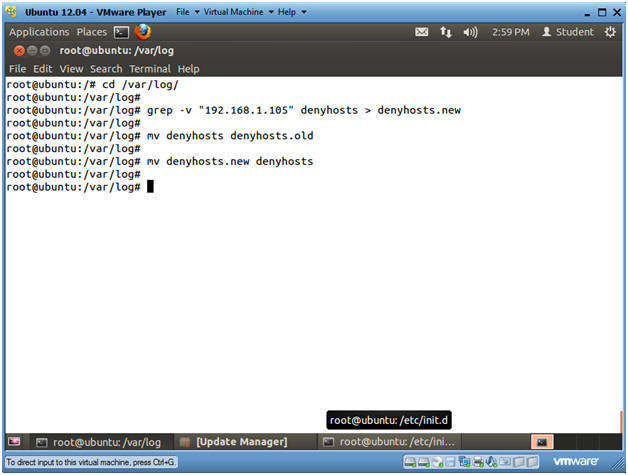
- cd /var/log/
- grep -v "192.168.1.105"
denyhosts > denyhosts.new
- Replace 192.168.1.105 with BackTrack's IP Address obtained in (Section 9, Step 2).
- mv denyhosts denyhosts.old
- mv denyhosts.new denyhosts
- Instructions:
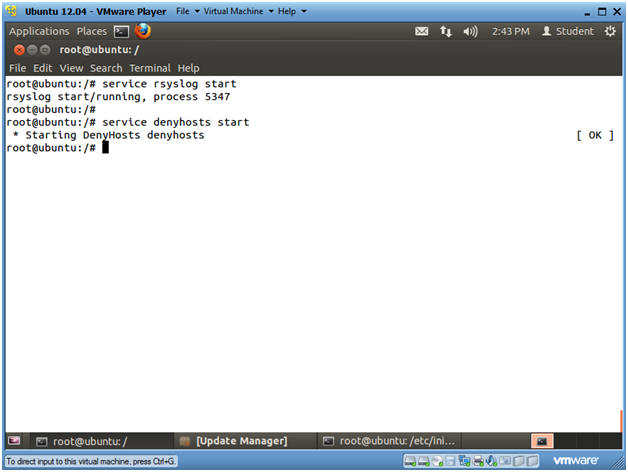
- Start syslog and denyhosts
- Instructions:
- service rsyslog start
- service denyhosts start
- Instructions:
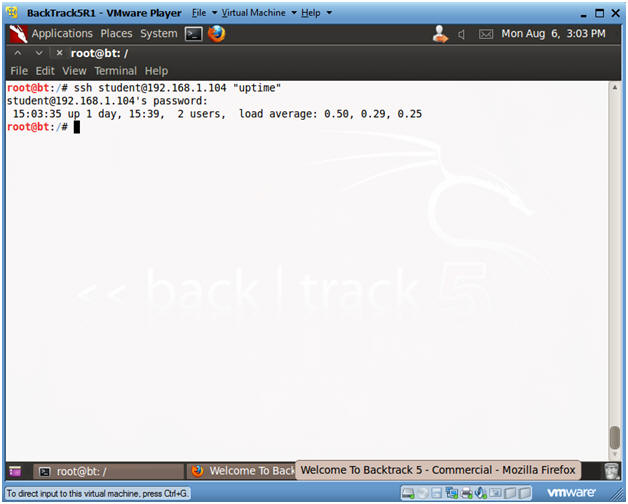
- Test SSH Connection from BackTrack to Ubuntu
- Note(FYI):
- Make sure you are on the BackTrack Server.
- Instructions:
- ssh
student@192.168.1.104
"uptime"
- If you do not have a student account on ubuntu, replace it with the system account you created in Lab 1.
- Replace 192.168.1.104 with Ubuntu's IP address you obtained in (Section 3, Step 3).
- Provide Password.
- ssh
student@192.168.1.104
"uptime"
- Note(FYI):