(Perl: Lesson 9)
{ Policy Part 2: Parsing /etc/ssh/sshd_config }
| Section 0. Background Information |
- What is /etc/ssh/sshd_config?
- /etc/ssh/sshd_config - OpenSSH SSH daemon configuration file. sshd reads configuration data from /etc/ssh/sshd_config. The file contains keyword-argument pairs, one per line. Lines starting with `#' and empty lines are interpreted as comments
- LogLevel - Gives the verbosity level that is used when logging messages from sshd The possible values are: QUIET, FATAL, ERROR, INFO, VERBOSE, DEBUG, DEBUG1, DEBUG2 and DEBUG3. The default is INFO. DEBUG and DEBUG1 are equivalent. DEBUG2 and DEBUG3 each specify higher levels of debugging output..
- PermitEmptyPasswords - When password authentication is allowed, it specifies whether the server allows login to accounts with empty password strings. The default is ``no''.
- X11Forwarding - Specifies whether X11 forwarding is permitted. The argument must be ``yes'' or ``no'' The default is ``no''. When X11 forwarding is enabled, there may be additional exposure to the server and to client displays if the sshd proxy display is configured to listen on the wildcard address.
- UsePAM - Enables the Pluggable Authentication Module interface. If set to ``yes'' this will enable PAM authentication using ChallengeResponseAuthentication and PAM account and session module processing for all authentication types.
- Getting Perl
- For the purposes of these perl lesson, I will be using a perl package that comes standard on Backtrack, Ubuntu and most flavors of Linux and Unix.
- However, if you are using Windows, instead
of a Linux, Unix or MAC operating system, you still have options.
- Pre-Requisite
-
Lab
Notes
- In this lab we will do the following:
- We will download a basic perl program that extracts the following keyword-argument pairs: LogLevel, PermitEmptyPasswords, and X11Forwarding.
- The program will provide extraction examples using split.
- In this lab we will do the following:
- Legal Disclaimer
- As a condition of your use of this Web site, you warrant to computersecuritystudent.com that you will not use this Web site for any purpose that is unlawful or that is prohibited by these terms, conditions, and notices.
- In accordance with UCC § 2-316, this product is provided with "no warranties, either express or implied." The information contained is provided "as-is", with "no guarantee of merchantability."
- In addition, this is a teaching website that does not condone malicious behavior of any kind.
- Your are on notice, that continuing and/or using this lab outside your "own" test environment is considered malicious and is against the law.
- © 2013 No content replication of any kind is allowed without express written permission.
| Section 1. Login to BackTrack |
- Start Up VMWare Player
- Instructions:
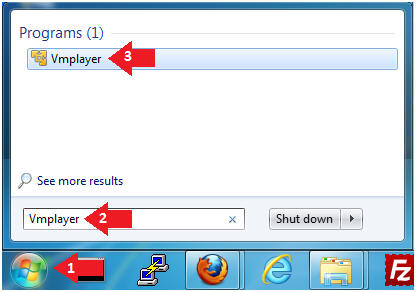
- Click the Start Button
- Type Vmplayer in the search box
- Click on Vmplayer
-
- Instructions:
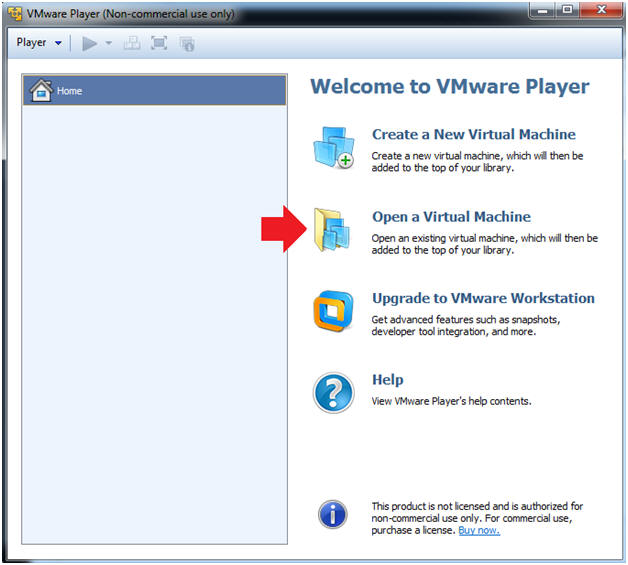
- Open a Virtual Machine
- Instructions:
- Click on Open a Virtual Machine
-
- Instructions:
- Open the BackTrack5R1 VM
- Instructions:
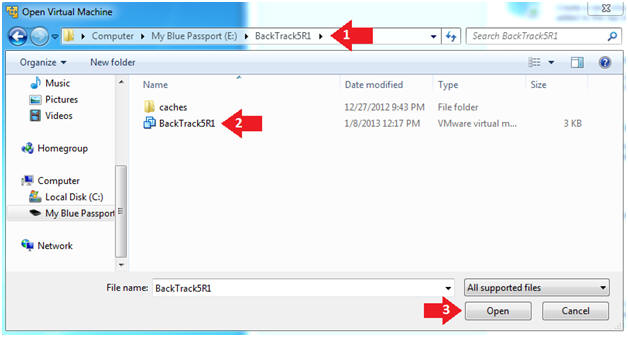
- Navigate to where the BackTrack5R1 VM is located
- Click on on the BackTrack5R1 VM
- Click on the Open Button
-
- Instructions:
- Edit the BackTrack5R1 VM
- Instructions:
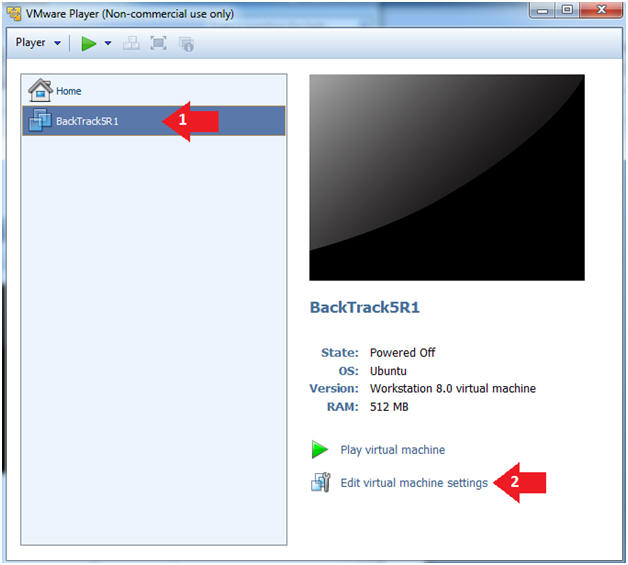
- Select BackTrack5R1 VM
- Click Edit virtual machine settings
-
- Instructions:
- Edit Virtual Machine Settings
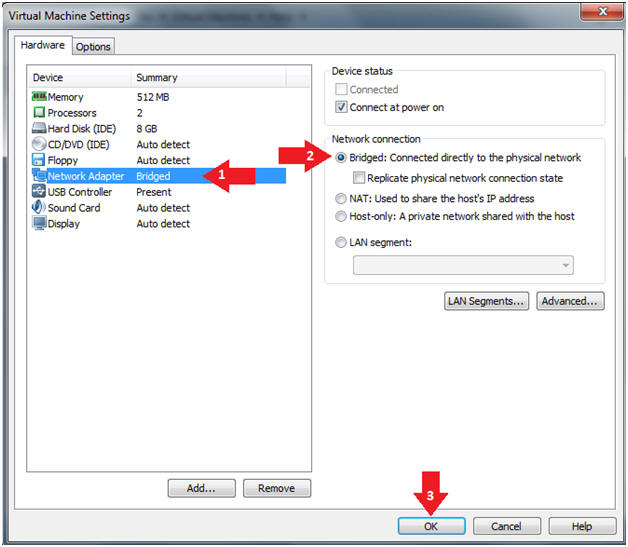
- Instructions:
- Click on Network Adapter
- Click on the Bridged Radio button
- Click on the OK Button
- Instructions:
- Play the BackTrack5R1 VM
- Instructions:
- Click on the BackTrack5R1 VM
- Click on Play virtual machine
-
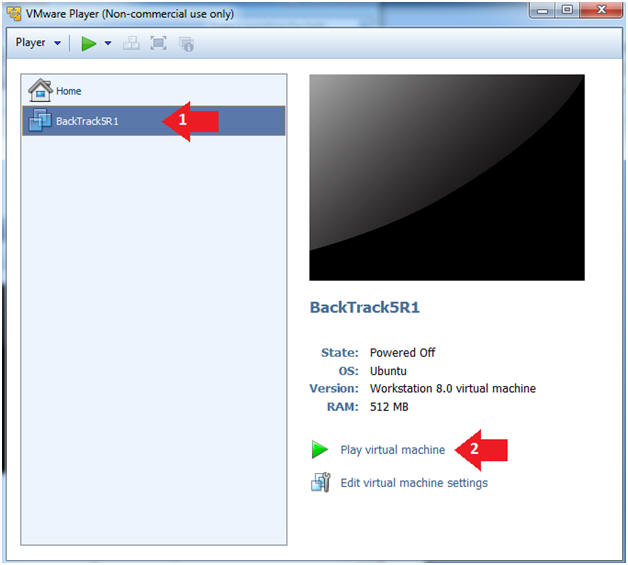
- Instructions:
- Login to BackTrack
- Instructions:
- Login: root
- Password: toor or <whatever you changed it to>.
-
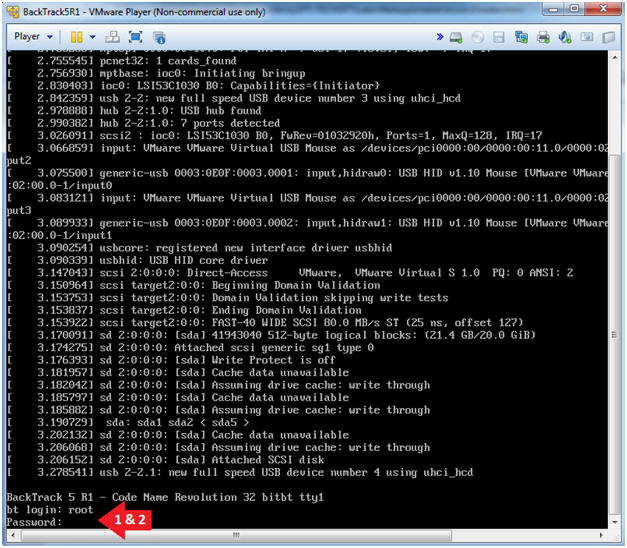
- Instructions:
- Bring up the GNOME
- Instructions:
- Type startx
-
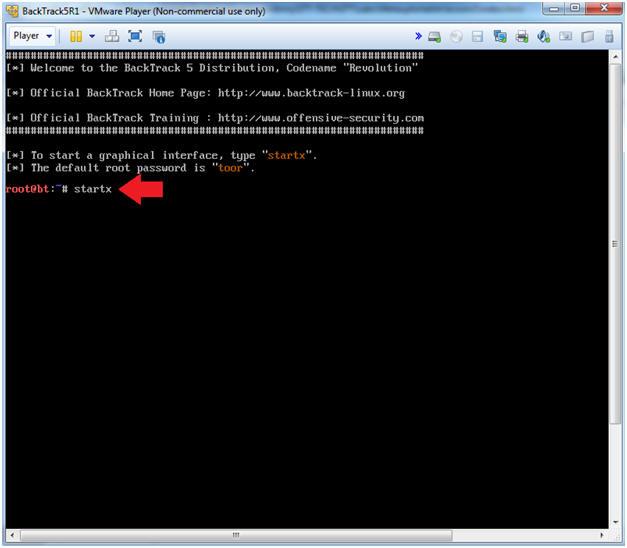
- Instructions:
| Section 2. Bring up a console terminal |
- Start up a terminal window
- Instructions:
- Click on the Terminal Window
- Instructions:
- Obtain the IP Address
- Instructions:
- ifconfig -a
- Note(FYI):
- My IP address 192.168.1.111.
- In your case, it will probably be different.
-
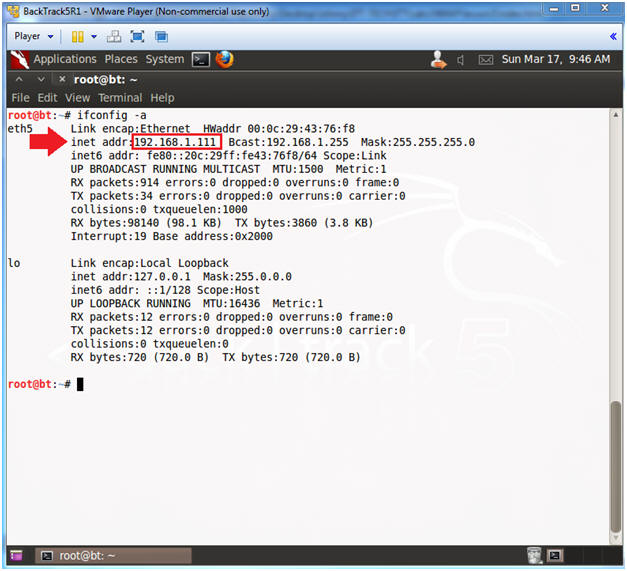
- Instructions:
| Section 3. Download scan_sshd_config.pl |
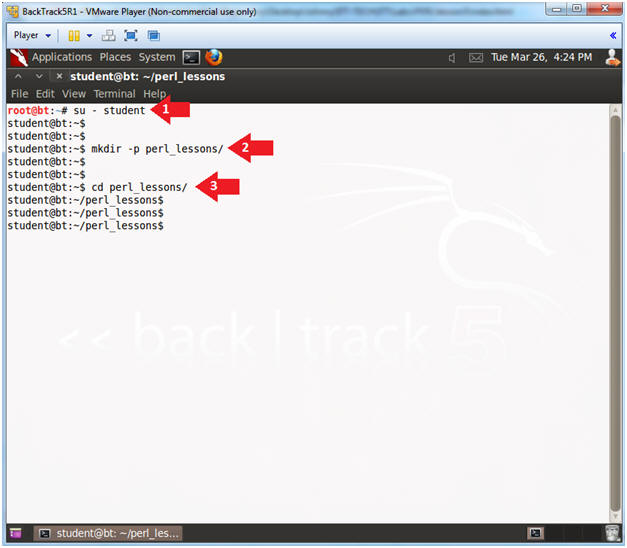
- Become the student user and make a directory
- Instructions:
- su - student
- mkdir -p perl_lessons
- cd perl_lessons
- Instructions:
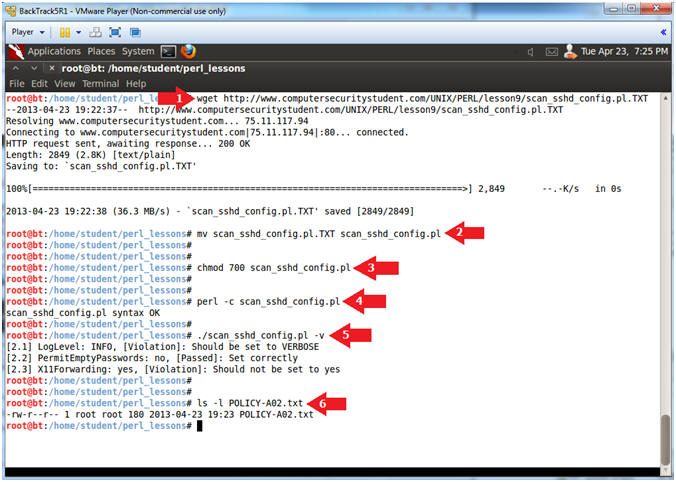
- Download scan_sshd_config.pl
- Instructions:
- wget http://www.computersecuritystudent.com/UNIX/PERL/lesson9/scan_sshd_config.pl.TXT
- mv scan_sshd_config.pl.TXT scan_sshd_config.pl
- chmod 700 scan_sshd_config.pl
- perl -c scan_sshd_config.pl
- ./scan_sshd_config.pl -v
- ls -l POLICY-A02.txt
- Instructions:
| Section 4. Analyze The Code |
- SheBang Directive
- Instructions:
- vi scan_sshd_config.pl
- :set nu
- Press the <Enter> key
- Note(FYI):
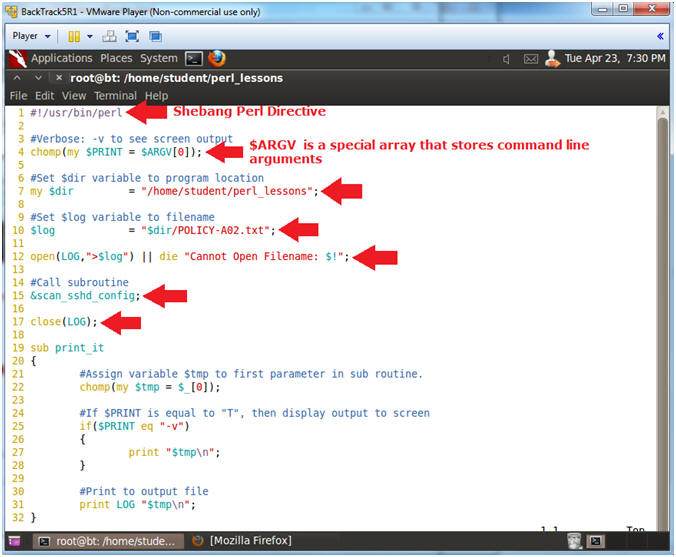
- Line 1: #!/usr/bin/perl
- #! - is called the SheBang Directive. SheBang is an interpreter directive that tells Linux to load the following program.
- /usr/bin/perl - is the Perl Interpreter. SheBang tells the program loader to run the Perl Interpreter.
- Line 4: chomp(my $PRINT = $ARGV[0]);
- $ARGV is a special perl array to receive command line arguments.
- $PRINT will be used to tell the program to output data to the screen.
- Line 7: my $dir = "/home/student/perl_lessons";
- Set the $dir variable to the directory location of the program.
- Line 10: $log = "$dir/POLICY-A02.txt";
- Set the $log variable to the output file name.
- Line 12: open(LOG,">$log") || die
"Cannot Open Filename: $!";
- Open the log file POLICY-A02.txt. LOG is the filehandle name. The greater than operator (>) mean to write to output.
- Line 15: &scan_sshd_config;
- Execute the subroutine scan_sshd_config.
- Line 17: close(LOG);
- Close the filehandle LOG, which is log file POLICY-A02.txt.
- Line 1: #!/usr/bin/perl
- Instructions:
- Explaining Lines 19 through 32
- Instructions:
- Arrow down to line 19
- Note(FYI):
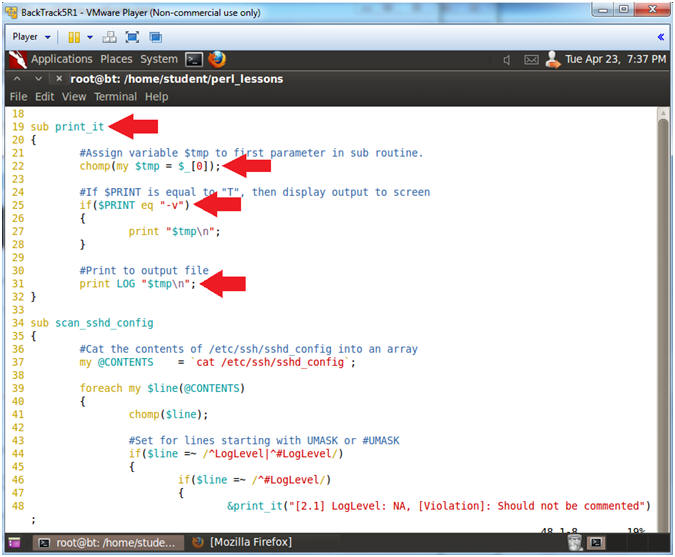
- Line 4, 20 & 32: sub print_it
- This subroutine has two actions: (1) Print to Output (line 31), and (2) Print to Screen (Lines 25 to 28).
- Line 22: chomp(my $tmp = $_[0]);
- Assign variable $tmp to first parameter.
- Line 25 - 28: if($PRINT eq "-v")
- If $PRINT is equal to -v, then print output to screen.
- Line 31: print LOG "$tmp\n";
- Print output to the filehandle LOG, which means print to the output file POLICY-A01.txt.
- Line 4, 20 & 32: sub print_it
- Instructions:
- Explaining Lines 34 through 88
- Instructions:
- Arrow down to line 34
- Note(FYI):
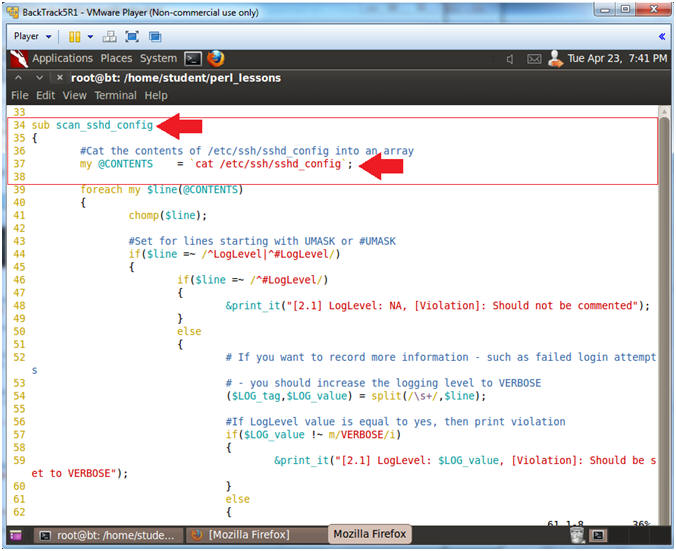
- Line 34: sub scan_sshd_config
- The scan_sshd_config subroutine scans the /etc/ssh/sshd_config file.
- Line 37: my @CONTENTS = `cat /etc/ssh/sshd_config`;
- This cats the contents of the /etc/ssh/sshd_config file into an array.
- Line 34: sub scan_sshd_config
- Instructions:
- Explaining Lines 38 through 42
- Instructions:
- Arrow down to line 39
- Note(FYI):
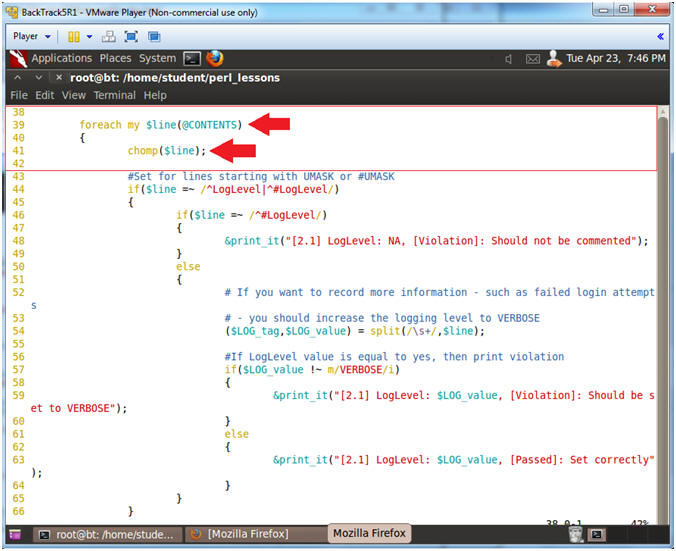
- Line 39: foreach my $line (@CONTENTS)
- This is a foreach loop. We will go through the array @CONTENTS line by line. Remember the @CONTENTS array contains the /etc/login.defs file.
- Line 41: chomp($line);
- Perl has a built in function called chomp that removes any end of line characters.
- Line 39: foreach my $line (@CONTENTS)
- Instructions:
- Explaining Lines 43 through 66
- Instructions:
- Arrow down to line 44
- Note(FYI):
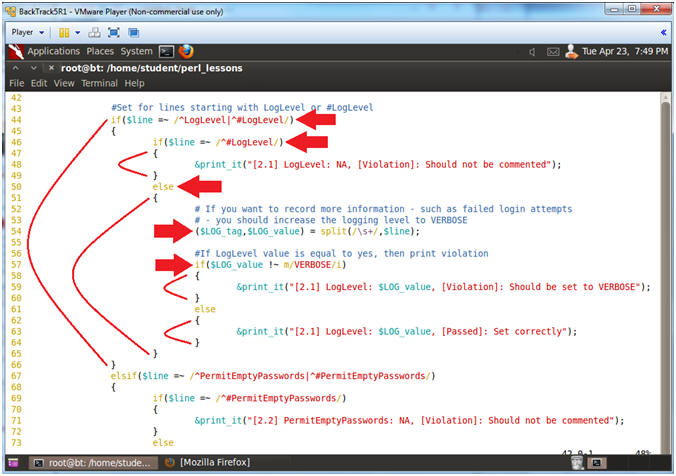
- Line 44: if($line =~ /^LogLevel|^#LogLevel/)
- Find a line that starts with either LogLevel OR #LogLevel. "^" means starts withs. "||" means OR.
- Line 46-49: if($line =~ /^#LogLevel/)
- If line starts with #LogLevel, then display Comment Out Violation.
- Line 50: else
- If line does not start with #LogLevel, then go else clause.
- Line 54: ($LOG_tag,$LOG_value) =
split(/\s+/,$line);
- Use the split function extract the LogLevel tag and value based on one or many white space (\s+) as a delimiter.
- Line 57: if($LOG_value !~ m/VERBOSE/i)
- If the extracted $LOG_value does not contain the string VERBOSE, then print violation.
- If the extracted $LOG_value does contain the string VERBOSE, then print passed.
- Line 44: if($line =~ /^LogLevel|^#LogLevel/)
- Instructions:
- Explaining Lines 67 through 88
- Instructions:
- Arrow down to line 67
- Note(FYI):
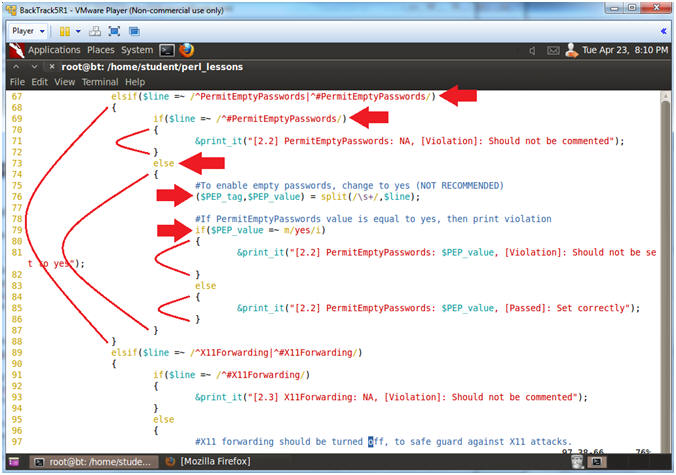
- Line 67: elsif($line =~
/^PermitEmptyPasswords|^#PermitEmptyPasswords/)
- Find a line that starts with either PermitEmptyPasswords OR #PermitEmptyPasswords. "^" means starts withs. "||" means OR.
- Line 69-72: if($line =~ /^#PermitEmptyPasswords/)
- If line starts with #PermitEmptyPasswords, then display Comment Out Violation.
- Line 73: else
- If line does not start with #PermitEmptyPasswords, then go else clause.
- Line 76: ($PEP_tag,$PEP_value) =
split(/\s+/,$line);
- Use the split function extract the PermitEmptyPasswords tag and value based on one or many white space (\s+) as a delimiter.
- Line 79: if($PEP_value =~ m/yes/i)
- If the extracted $PEP_value does contain the string YES, then print violation.
- If the extracted $PEP_value does contain the string YES, then print passed.
- Line 67: elsif($line =~
/^PermitEmptyPasswords|^#PermitEmptyPasswords/)
- Instructions:
- Explaining Lines 89 through 111
- Instructions:
- Arrow down to line 89
- Note(FYI):
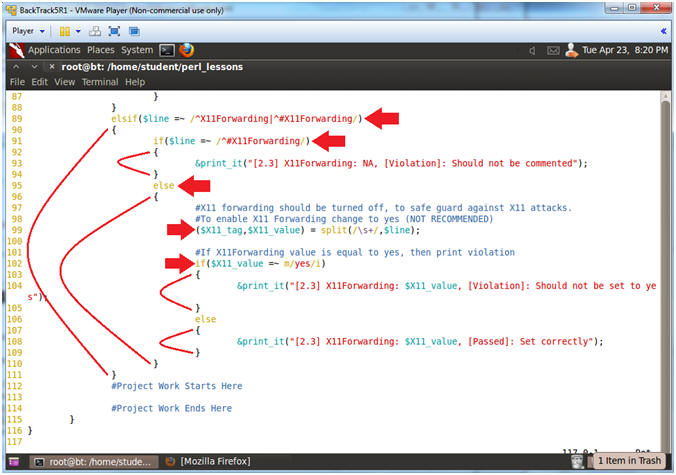
- Line 89: elsif($line =~
/^X11Forwarding|^#X11Forwarding/)
- Find a line that starts with either X11Forwarding OR #X11Forwarding. "^" means starts withs. "||" means OR.
- Line 91-94: if($line =~
/^#X11Forwarding/)
- If line starts with #X11Forwarding, then display Comment Out Violation.
- Line 95: else
- If line does not start with #X11Forwarding, then go else clause.
- Line 99: ($X11_tag,$X11_value) =
split(/\s+/,$line);
- Use the split function extract the X11Forwarding tag and value based on one or many white space (\s+) as a delimiter.
- Line 102: if($X11_value =~ m/yes/i)
- If the extracted $X11_value does contain the string YES, then print violation.
- If the extracted $X11_value does contain the string YES, then print passed.
- Line 89: elsif($line =~
/^X11Forwarding|^#X11Forwarding/)
- Instructions:
- Instructions:
- Arrow down to line 115
- Note(FYI):
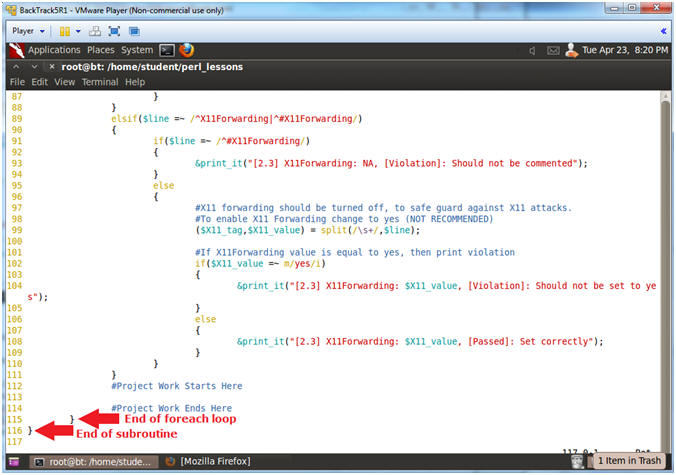
- Line 115: }
- End of foreach loop
- Line 116: }
- End of subroutine
- Line 115: }
- Save and Quit
- Instructions:
- Press the <Esc> key
- :q!
- Press the <Enter> key
- Instructions:
| Section 5. Proof of Lab |
- Project
- Instructions:
- cp scan_sshd_config.pl scan_sshd_config.BKP
- Your project is to write an if-clause that interrogate the string "UsePAM" the same way the program interrogates the string LogLevel, PermitEmptyPasswords and X11Forwarding.
- vi scan_sshd_config.pl
- After the line that contains "#Project
Work Starts Here", place the below code.
-
elsif($line =~ /^UsePAM|^#UsePAM/) { if($line =~ /^#UsePAM/) { &print_it("[2.4] UsePAM: NA, [Violation]: Should not be commented"); } else { ($PAM_tag,$PAM_value) = split(/\s+/,$line); # Prevent ssh login from bypassing pam if($PAM_value !~ m/yes/i) { &print_it("[2.4] UsePAM: $PAM_value, [Violation]: Should be set to yes"); } else { &print_it("[2.4] UsePAM: $PAM_value, [Passed]: Set correctly"); } } }
-
- Press <Esc>
- :wq!
- Instructions:
- Proof of Lab
- Instructions
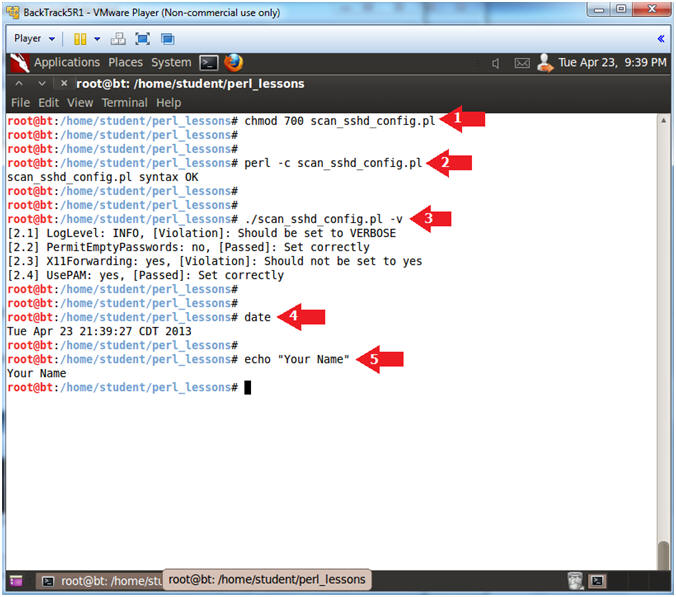
- chmod 700 scan_sshd_config.pl
- perl -c scan_sshd_config.pl
- ./scan_sshd_config.pl -v
- date
- echo "Your Name"
- Put in your actual name in place of "Your Name"
- e.g., echo "John Gray"
-
Proof Of Lab
Instructions:
- Press the <Ctrl><Alt> keys simultaneously
- Press the <PrtScn> key
- Paste into a word document
- Upload to Moodle
- Instructions